Imagine walking into a patient’s room and seeing them struggling to breathe, their chest heaving with each labored breath. Their skin is clammy and they cough up phlegm, their eyes filled with fear and discomfort. This is a reality for many nurses who encounter patients suffering from pneumonia, a serious lung infection that can be life-threatening. Understanding the complexities of pneumonia and developing a comprehensive care plan is crucial for providing effective and empathetic care.
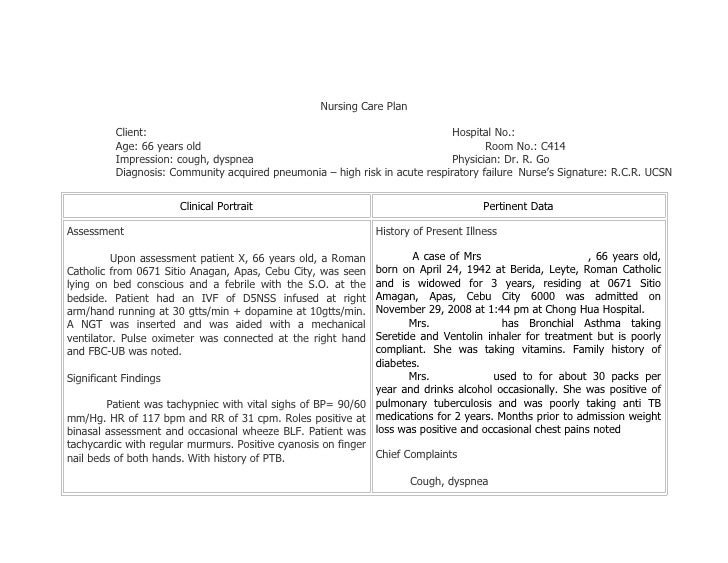
Image: www.slideshare.net
This article will delve into the world of pneumonia, providing nurses with a detailed nursing care plan in a PowerPoint presentation format. We will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this common respiratory ailment, along with the essential aspects of patient care, including medication administration, breathing exercises, and supportive measures. We aim to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to effectively manage pneumonia patients and navigate their recovery journey.
Understanding Pneumonia: A Closer Look
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by an infection, usually bacterial, viral, or fungal. This infection leads to the buildup of fluid and pus in the air sacs within the lungs, known as alveoli. This fluid fills the air sacs, making it difficult for oxygen to reach the bloodstream, leading to a range of symptoms including shortness of breath, fever, and cough.
The most common types of pneumonia include:
- Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): This type of pneumonia is contracted outside of a hospital or healthcare facility, typically from viruses or bacteria in the community.
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP): As the name implies, HAP is developed in a hospital setting, often during a hospital stay for another condition. It is typically resistant to antibiotics and can be more serious.
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP): This type of pneumonia occurs in patients who are intubated and on a mechanical ventilator. The risk of VAP is high due to the presence of a breathing tube and the weakened immune system.
Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia: A Comprehensive Guide
Developing a comprehensive nursing care plan is essential for managing patients with pneumonia. This plan should address the patient’s individual needs and include a variety of interventions to promote optimal recovery. The care plan should be tailored to the specific type of pneumonia, the patient’s age, underlying medical conditions, and response to treatment.
A well-structured pneumonia nursing care plan will incorporate the following key elements:
- Assessment: This involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s current condition, including their respiratory status, vital signs, and overall wellbeing. It also includes gathering information about their medical history, medication list, and social support.
- Diagnosis: Careful diagnosis allows nurses to identify the underlying cause of the pneumonia, which is essential for determining the appropriate treatment. Common nursing diagnoses for patients with pneumonia may include ineffective airway clearance, impaired gas exchange, and activity intolerance.
- Planning: This involves developing realistic and measurable goals for the patient. Goals should focus on improving their respiratory status, alleviating their symptoms, and ultimately achieving a full recovery.
- Implementation: This includes implementing the planned interventions, such as administering medications, providing oxygen therapy, encouraging deep breathing exercises, and promoting rest.
- Evaluation: This involves regularly monitoring the patient’s progress and assessing the effectiveness of the interventions implemented. Any changes in the patient’s condition should be documented and reported to the physician.
Key Interventions for Pneumonia Patients:
A nursing care plan for pneumonia, especially in a PPT format, should highlight the core interventions that lead to patient improvement. These are essential to manage symptoms, promote healing, and support the patient’s overall well-being.
Key interventions should include:
- Respiratory Support: The primary focus of care for pneumonia is improving respiratory function and oxygenation. This often involves providing supplemental oxygen through a nasal cannula or a face mask. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation may be required to assist with breathing.
- Medication Administration: Antibiotics are typically used to treat bacterial pneumonia. Viral pneumonia is often treated with antiviral medications. Pain relievers and anti-fever medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and enhance comfort.
- Positioning: Elevating the patient’s head of bed to 30-45 degrees can improve lung expansion and reduce stress on the respiratory system. Regular position changes can also help mobilize secretions and prevent fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Fluid Management: Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for recovery. Encourage patients to drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to thin mucus and aid in clearance. However, fluid restrictions may be needed for patients with heart failure or other conditions.
- Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is crucial for supporting the body’s immune system and promoting healing. Encourage patients to consume high-protein, high-calorie meals and snacks that are easy to digest. However, it is essential to consider individual dietary needs and limitations.
- Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises and coughing techniques are essential for clearing airway secretions, improving lung capacity, and preventing complications. It is vital to educate the patient on proper techniques and encourage regular practice.
- Rest and Activity: Rest is paramount for recovery, allowing the body to focus on healing. However, early mobilization and gentle activity are also important to prevent muscle weakness and maintain cardiovascular health. It is essential to assist patients with their activities and monitor their response.
- Psychosocial Support: Patients with pneumonia may experience anxiety, fear, and discomfort. Providing emotional support, encouraging open communication, and addressing their concerns can enhance overall well-being and promote healing.

Image: www.youtube.com
Tips for Creating a High-Quality Nursing Care Plan PPT
A well-designed nursing care plan PPT is a valuable tool for communication, education, and documentation. It is important to present information in a clear, concise, and visually appealing manner.
Here are some key tips for creating a high-quality PPT for pneumonia care planning:
- Use a Consistent Template: Employ a consistent template for all slides to maintain visual unity and professionalism. Use clear and easy-to-read fonts, and ensure text is large enough to be easily visible.
- Utilize High-Quality Images: Include relevant images and diagrams to illustrate key concepts and enhance learning. Ensure that images are high resolution and properly cited.
- Keep It Concise: Focus on the essential information and avoid overwhelming the viewer with too much text. Use bullet points and concise sentences to facilitate understanding, and ensure proper formatting for readability.
- Include Relevant Data: Incorporate relevant data, such as guidelines, treatment protocols, and statistics, to provide a strong scientific foundation. Keep in mind the intended audience and their level of expertise when including this data.
- Practice Effective Storytelling: Tailor the PPT to tell a compelling story about the management of pneumonia patients. Use real-world examples, patient narratives, and case studies to engage the audience.
FAQ: Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding pneumonia nursing care plans and patient management:
Q: What is the most important factor in preventing pneumonia?
A: Preventing pneumonia relies on a multi-pronged approach:
- Hand Hygiene: Washing hands frequently with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizer is essential to minimize the spread of viruses and bacteria.
- Vaccination: The pneumococcal vaccine is highly effective in preventing pneumococcal pneumonia, especially in the elderly, young children, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can boost the immune system and reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoidance of Smoke and Pollutants: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke significantly increase the risk of pneumonia. It is important to avoid these risk factors and minimize exposure to environmental pollutants.
Q: How can I tell if a patient with pneumonia is getting worse?
A: Monitor the patient’s vital signs closely. Look for changes in respiratory rate, oxygen saturation levels, heart rate, and blood pressure. Any increase in difficulty breathing, chest pain, altered mental status, or worsening cough should be immediately reported to the physician.
Q: What are the potential complications of pneumonia?
A: Pneumonia can cause severe complications, particularly for older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions. These complications may include:
- Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to infection harms its own tissues and organs.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A serious lung injury that causes fluid buildup in the alveoli, leading to respiratory failure.
- Lung Abscess: A collection of pus in the lungs, which can be caused by bacterial pneumonia.
- Pleural Effusion: Accumulation of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart, which can be caused by pneumonia in some cases.
Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia Ppt
Conclusion
A comprehensive nursing care plan for pneumonia is essential for providing effective and compassionate care to patients with this common respiratory infection. It is important to remember that every patient’s needs are unique. By understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and potential complications of pneumonia, nurses can develop tailored care plans that prioritize patient well-being and promote optimal recovery.
Are you interested in learning more about pneumonia or developing your own nursing care plans using PowerPoint presentations? Share your thoughts and questions in the comment section below.





