Have you ever wondered how mental health professionals understand and respond to the complex emotional landscape of their patients? Imagine being able to step into the mind of someone struggling with anxiety, depression, or psychosis. While that might sound like a feat of magic, it’s actually a crucial process known as process recording, a tool used by psychiatric nurses to gain invaluable insights into their patients’ experiences. This detailed form of documentation isn’t just about recording facts; it’s about understanding the nuances of mental health, the unspoken emotions, and the intricate dance of communication.

Image: www.coursehero.com
Process recording is a valuable technique that psychiatric nurses use to meticulously document patient interactions. It’s more than just a simple log of what was said; it’s a comprehensive record of the entire interaction, including both verbal and nonverbal cues, emotional responses, and the nurse’s own thoughts and feelings. This detailed documentation serves as a powerful tool for reflection, analysis, and ultimately, enhancing patient care. It allows nurses to delve into the complexities of mental health, unraveling the unspoken emotions and understanding the true meaning behind words – a practice that is essential for effective therapeutic interventions in psychiatric nursing.
Delving into the World of Process Recording
What is Process Recording?
Process recording in psychiatric nursing is a systematic method of documenting therapeutic interactions with patients. It goes beyond simply writing down what was said; it captures the entirety of the interaction, including both the patient’s and the nurse’s verbal and nonverbal behaviors. This detailed documentation serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of the patient’s mental state, identifying patterns in communication, and developing effective therapeutic strategies.
Key Components of Process Recording
Process recording involves capturing a variety of elements that contribute to the overall picture of the therapeutic interaction. These key components include:
- Patient’s Verbalizations: This includes the actual words spoken by the patient, their tone of voice, and any pauses or hesitations. It’s essential to capture the nuances of language, as these can reveal much about the patient’s emotional state.
- Patient’s Nonverbal Behaviors: Observing body language – facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact – can provide valuable insights into the patient’s feelings and level of engagement. For example, a patient who is fidgeting or avoiding eye contact might be feeling anxious or uncomfortable.
- Nurse’s Responses: The nurse’s verbal and nonverbal responses are also recorded. This includes the specific words used, the tone of voice, and any gestures or facial expressions. It’s crucial to reflect on how the nurse’s responses might be influencing the patient’s behavior.
- Nurse’s Observations: This includes any observations made by the nurse about the patient’s appearance, demeanor, or environment that might be relevant to the interaction. For example, noticing that a patient is dressed in disheveled clothes could suggest a decline in self-care.
- Nurse’s Thoughts and Feelings: While subjective, the nurse’s own thoughts and feelings during the interaction are valuable for self-reflection and understanding their own biases and reactions. This helps the nurse maintain objectivity and provide effective care.
- Analysis: After the interaction, the nurse analyzes the recording, looking for patterns, themes, and insights into the patient’s behavior and communication. This step is crucial for developing a deeper understanding of the patient’s mental health and informing future therapeutic interactions.
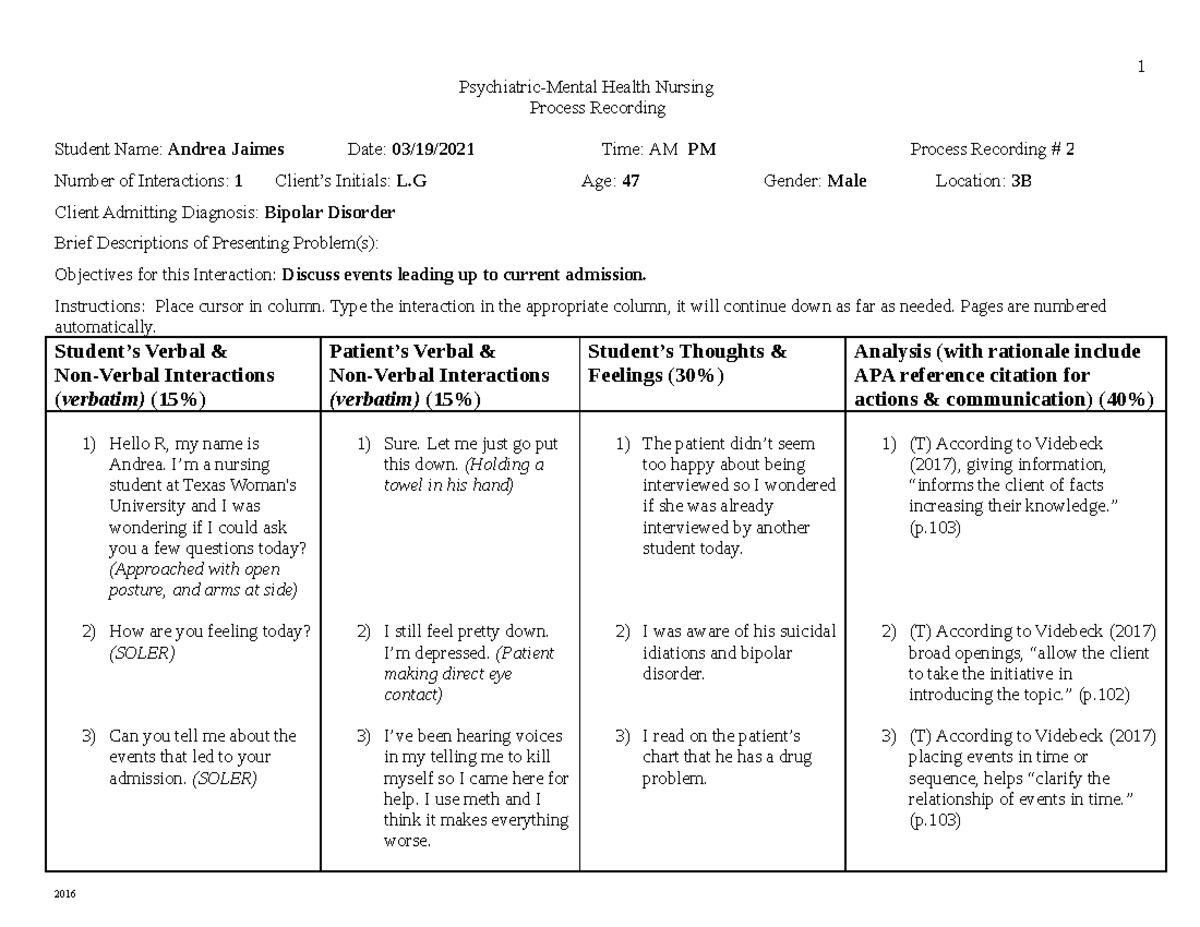
Image: www.studocu.com
The Importance of Process Recording
Process recording plays a vital role in psychiatric nursing by providing several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Understanding of the Patient: By meticulously documenting the patient’s communication and behavior, nurses gain a deeper understanding of their mental state, triggers, and coping mechanisms. This knowledge is essential for developing individualized care plans.
- Improved Communication and Therapeutic Skills: Analyzing the process recording helps nurses identify their own communication patterns and areas for improvement. It allows them to refine their therapeutic skills and become more effective in building rapport and trust with patients.
- Objective Documentation and Evaluation: Process recordings provide a clear and objective record of the patient’s progress, allowing for effective evaluation of treatment plans and the identification of areas requiring adjustments.
- Professional Development and Collaboration: Process recordings serve as a valuable tool for sharing knowledge with other professionals. They can be used for supervision, case conferences, and peer review, facilitating collaboration and ensuring the highest quality of care.
A Real-World Example of Process Recording
To illustrate how process recording works in practice, let’s consider a fictional scenario involving a psychiatric nurse named Sarah and her patient, Mark, who is struggling with depression and anxiety. During a therapy session, Sarah observes the following:
Patient: (Sits slumped in chair, avoids eye contact) “I don’t know what’s wrong with me. I just feel so tired all the time, it’s like I have no energy to do anything.”
Nurse: (Maintains eye contact, nods empathetically) “It sounds like you’re feeling exhausted. Can you tell me more about what’s making you feel this way?”
Patient: (Sighs heavily, looks down at his hands) “I just feel like a failure. I can’t seem to hold down a job, my relationships are falling apart, and I’m constantly letting people down.”
Nurse: (Uses a gentle tone) “It sounds like you’re carrying a lot of pressure and disappointment. It’s understandable that you’re feeling overwhelmed. Can you tell me more about how these feelings are affecting your daily life?”
Patient: (Voice trembling slightly) “I just want to sleep all the time. I don’t even feel like taking care of myself. I’m afraid I’m going to lose everything.”
Nurse: (Uses a calm and reassuring voice) “I understand how frightening that must feel. It’s important to remember that you’re not alone in this. I’m here to support you. How can I help you find some relief today?”
Nurse’s Observations: Mark appears withdrawn, avoids eye contact, and exhibits slumped posture. He expresses feelings of hopelessness, failure, and fear of losing everything. He seems emotionally overwhelmed and lacks energy.
Nurse’s Thoughts and Feelings: I feel a strong sense of empathy for Mark. It’s heartbreaking to see him struggling so much. I want to provide him with reassurance and help him feel understood. I need to remain calm and professional to create a safe space for him to express his emotions.
By meticulously documenting this interaction, Sarah is able to gain valuable insights into Mark’s mental state and communication patterns. She can then use this information to develop a personalized care plan that addresses his specific needs and supports his recovery. This illustrative example highlights the importance of process recording in helping psychiatric nurses understand the complexities of mental illness, develop effective therapeutic strategies, and ultimately, improve patient outcomes.
Process Recording In Psychiatric Nursing Example
The Power of Process Recording in Psychiatric Nursing
Process recording is not simply a bureaucratic task; it’s a powerful tool that allows psychiatric nurses to truly connect with their patients on a deeper level. By capturing the nuances of communication and analyzing the dynamics of the therapeutic relationship, they gain insights that guide them in providing individualized and effective care. Through this process, they can empower patients to navigate the challenges of mental illness, build resilience, and find hope for a brighter future. In the world of psychiatric nursing, process recording serves as a bridge between theory and practice, fostering empathy, understanding, and ultimately, healing.
If you’re interested in learning more about process recording and its application in psychiatric nursing, there are numerous resources available online and in academic libraries. Explore these resources to deepen your understanding of this valuable tool and how it contributes to the well-being of patients struggling with mental health challenges.





