Navigating the complex world of government structures can feel like deciphering a foreign language. Often, we hear terms like “federal” and “unitary” tossed around, but few truly understand the profound distinctions between them. Imagine walking into a bustling marketplace, surrounded by vibrant vendors selling unique wares. Each stall represents a different system of governance, and understanding the differences between federation and unitary government is like learning to navigate this diverse marketplace of political ideas.
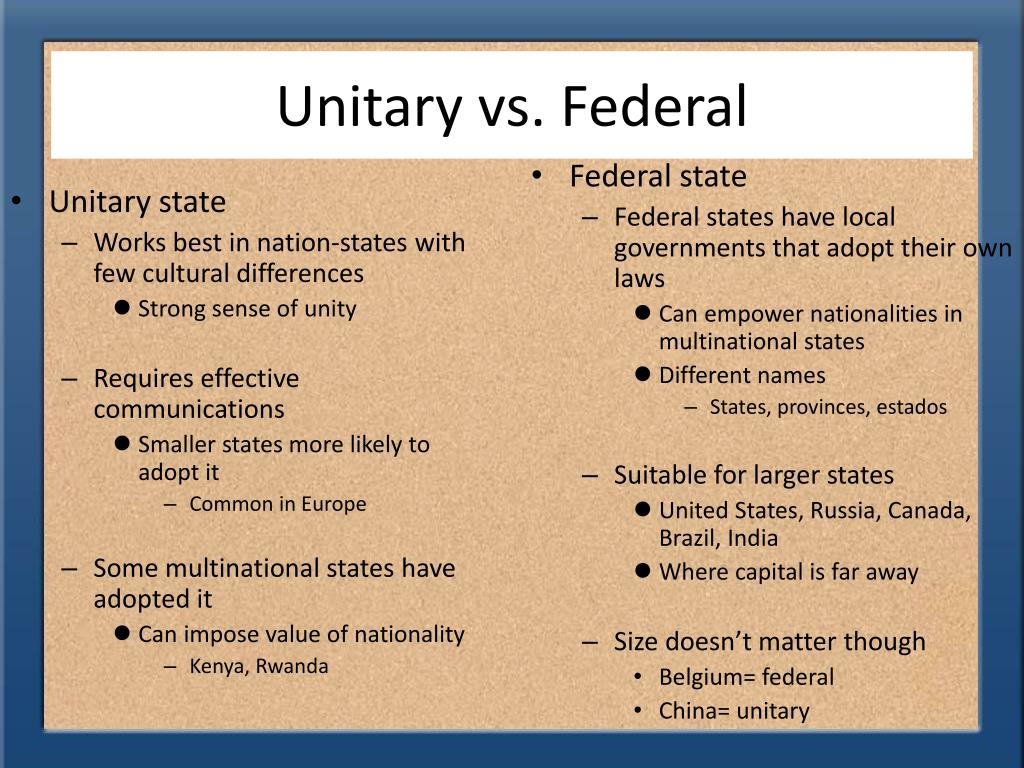
Image: www.slideserve.com
This guide will help you understand the fundamental differences between federations and unitary governments. We’ll explore how each structure shapes the power dynamic between central and regional authorities, highlighting the unique characteristics that define each system. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each, allowing you to navigate the complexities of political systems with confidence.
Understanding Federal and Unitary Governments: Defining the Terms
The Essence of Federalism
Federal governments are characterized by a division of power between a central authority and constituent units – often referred to as states, provinces, or regions. It’s like a shared governance model where a central government handles national-level affairs, while regional entities retain control over their internal matters. Think of it as a partnership where both levels of government have their distinct spheres of influence.
This division of power is typically enshrined in a constitution – a written document outlining the fundamental principles and rights of the country. In a federal system, the central government’s powers are usually limited to specific areas defined by the constitution, such as defense, foreign policy, and national currency. All other powers are left to the regional entities, allowing them to govern their own affairs.
The Unitary Government Model: Centralized Authority
A unitary government, in stark contrast to a federal structure, concentrates power within a single, central authority. Imagine a single, powerful entity wielding authority over the entire nation. This centralized system grants the central government the ultimate power to make decisions across all geographic and administrative units.
Unlike a federation, regional entities in a unitary government lack significant autonomy. They essentially act as extensions of the central authority, carrying out its directives and policies. While regional governments may handle certain local matters, their power is ultimately derived from and subject to the central government. Think of it as a hierarchical system where the central government is the top decision-maker.

Image: www.meritnation.com
Comparing Key Differences: Delving Deeper into Federated and Unitary Models
Distribution of Power: The Defining Factor
The most fundamental difference between federal and unitary systems lies in the way power is distributed. In a federation, power is shared between a central and regional governments. The constitution specifically outlines the limits and responsibilities of each level. In a unitary system, power is consolidated at the central level. Regional entities may have some administrative authority, but their actions are subject to the central government’s oversight.
Flexibility and Resilience: Adapting to Change
One of the key arguments in favor of federalism is its ability to cater to diverse needs and aspirations across different regions. Different regions often have unique cultural, economic, and social characteristics. A federal system allows for more flexible policy-making, responding to these varying needs. Unitary systems, on the other hand, tend to be more rigid, with policies flowing top-down from the central authority. This can lead to greater uniformity at the cost of addressing local specificities.
Accountability and Representation: Diverse Perspectives
Federalism fosters a more pluralistic political system by allowing regional entities to elect their own representatives and enact policies that are relevant to their local communities. This can lead to a more diverse representation of interests within the national government. In contrast, unitary systems may struggle with representation at the local level, as power is concentrated at the central level. This can create a disconnect between those in power and the people they govern.
Legislative Processes: Shaping Laws and Regulations
Federal systems typically involve bicameral legislatures, featuring both a national assembly representing the entire population and a chamber representing the states or regions. This bicameral structure creates an additional layer of checks and balances, ensuring that both national and regional viewpoints are considered in lawmaking. Unitary systems often have unicameral legislatures, where all representatives are elected by the entire population. While this simplifies the legislative process, it can limit regional representation.
Examples in the Real World: A Glimpse into Different Systems
To understand the practical implications of these systems, let’s examine a few prominent examples:
- United States: A prime example of a federal system. The US Constitution explicitly divides powers between the national government and individual states, granting immense autonomy to states in areas like education, law enforcement, and taxation.
- Canada: Another strong proponent of federalism. Canada divides power between the federal government and ten provinces and three territories, with each region having its own legislative assembly and governing powers.
- France: A classic example of a unitary system. Power is concentrated in the central government in Paris, which governs the entire nation. While regional entities (départements) have some administrative functions, their authority is derived from and ultimately subordinate to the central government.
- United Kingdom: A complex hybrid system that has evolved over time. While the UK is considered a unitary system, with the central government holding ultimate authority, its constituent parts (England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland) have varying degrees of autonomy.
The Future of Federated and Unitary Systems: Emerging Trends
Governments worldwide are constantly evolving in response to changing political and social dynamics. In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards decentralization within unitary systems. This includes granting more autonomy to regional entities and increasing their participation in decision-making processes. For example, Spain has witnessed a significant shift towards greater regional autonomy in recent decades.
However, it’s essential to recognize that the decentralization trend doesn’t necessarily signify a move towards federalism. In many cases, regional entities are granted more autonomy within the framework of a unitary system, and their power remains ultimately subject to the central government.
Expert Tips for Understanding Governmental Systems
Here are some tips to help you navigate the complexities of federal and unitary governments:
- Focus on the Constitution: The constitution is the defining document for any government, whether federal or unitary. It lays out the fundamental principles, powers, and responsibilities of different levels of government.
- Consider the Historical Context: Understanding the historical development of a country’s government system can provide invaluable insights into its structure and current dynamics.
- Engage with Local Politics: Pay attention to local politics and the activities of regional governments. This can provide a deeper understanding of how the government system operates at the grassroots level.
- Be a Critical Consumer of Information: It’s crucial to be discerning about information regarding government systems. Look for credible sources and critically evaluate different perspectives.
FAQs: Clearing Up Common Questions
Q: What are the advantages of a federal system?
A: Federalism offers greater flexibility in addressing diverse regional needs, promotes political pluralism, and strengthens regional representation. It also provides a framework for decentralizing power and fostering greater accountability at the local level.
Q: What are the advantages of a unitary system?
A: Unitary systems can ensure strong central authority, simplifying policy implementation across the nation. This centralized structure can be beneficial in promoting national unity and streamlining decision-making processes.
Q: Can a country transition from a unitary to a federal system?
A: Yes, countries can transition from unitary to federal systems, but this process is complex and often involves constitutional amendments or major political reforms.
Q: Are there any hybrid systems combining elements of both federal and unitary models?
A: Yes, many countries have hybrid systems that blend aspects of both models. For example, the United Kingdom, while considered a unitary system, grants significant autonomy to some of its constituent parts.
Difference Between Federation And Unitary Government
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamental differences between federal and unitary systems is essential for navigating the complexities of global politics and governance. Each system offers unique strengths and weaknesses, shaping the power dynamics between central and regional authorities. By exploring the historical context, analyzing current examples, and engaging with different perspectives, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse ways in which societies organize themselves and make decisions.
Are you interested in learning more about specific examples of federal and unitary systems? Would you like to explore the historical evolution of these government models? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!





