Imagine a patient struggling to catch their breath, their skin pale and clammy, their heart racing. This is the reality of impaired tissue perfusion – a condition where the blood supply to tissues is inadequate, leading to a cascade of complications. As a nurse, I vividly recall the day I encountered a patient experiencing severe peripheral arterial disease, their toes turning black and numb. The gravity of the situation ignited a fire in me to understand and manage this critical condition. This experience shaped my passion for developing comprehensive nursing care plans for patients with impaired tissue perfusion, and I want to share my knowledge with you.
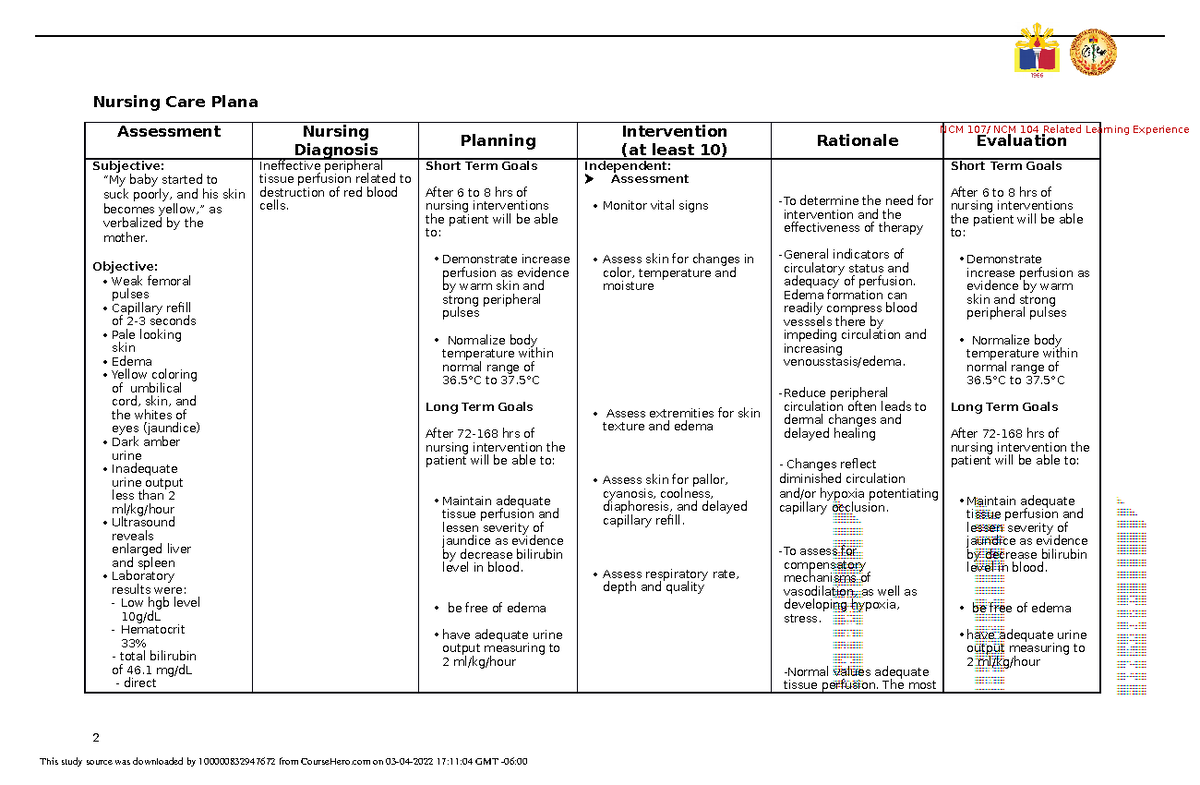
Image: www.studocu.com
This article delves into the intricacies of impaired tissue perfusion, exploring its causes, manifestations, and the crucial role of nursing intervention. We will unravel the complexities of this condition, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of how to provide optimal care to your patients. By the end, you will have a solid grasp of the nursing care plan, including assessment, interventions, and evaluation, empowering you to effectively manage patients with impaired tissue perfusion.
Understanding Impaired Tissue Perfusion: A Vital Concept
Impaired tissue perfusion refers to a condition where the blood flow to tissues is insufficient to meet metabolic demands. This can occur due to various factors, including cardiovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, trauma, and even prolonged immobility. The consequences of impaired tissue perfusion can range from minor discomfort to life-threatening complications. It’s crucial for nurses to recognize the early signs and symptoms of impaired tissue perfusion to initiate appropriate interventions and prevent irreversible damage.
The severity of impaired tissue perfusion depends heavily on the affected tissue, the cause, and the duration of the blood flow disruption. The underlying principle is that when blood flow is compromised, the tissue experiences a shortage of oxygen and nutrients, while waste products accumulate. This can lead to a cascade of potentially harmful events, including cell death, organ dysfunction, and even sepsis.
Key Elements of the Impaired Tissue Perfusion Nursing Care Plan
Assessment and Diagnosis
The foundation of effective care rests on a thorough assessment. Nurses play a crucial role in identifying and evaluating patients at risk for or experiencing impaired tissue perfusion. Their assessment encompasses a comprehensive evaluation of vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature. Nurses also meticulously examine the patient’s skin for changes in color, temperature, capillary refill, peripheral pulses, and edema. They observe for any signs of pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected extremities. Additional assessments may include laboratory tests, such as complete blood count, blood glucose levels, and serum electrolytes.
Once the assessment is complete, the nurse collaborates with the healthcare team to establish a diagnosis and prioritize interventions. The diagnosis of impaired tissue perfusion often requires a multi-disciplinary approach, including physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. The nursing care plan is then tailored to address the specific needs of the individual patient.
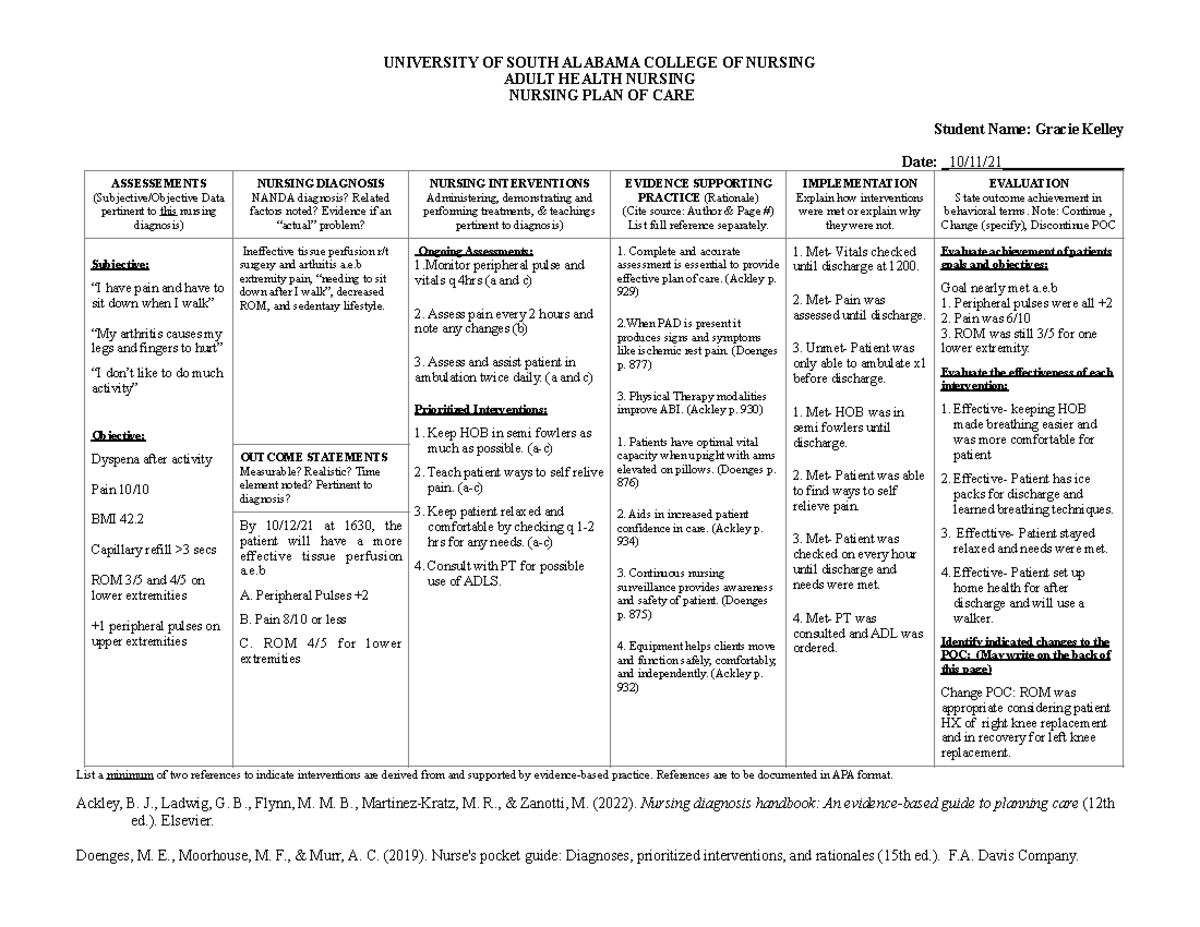
Image: www.studocu.com
Interventions: Optimizing Blood Flow and Tissue Health
Interventions for impaired tissue perfusion are multifaceted and aim to address the underlying cause of the condition while promoting adequate blood flow and tissue health. These interventions vary depending on the specific cause and severity of the condition. However, common nursing interventions include:
- Positioning: Elevating the affected limb above the heart can enhance venous return and reduce edema. This simple intervention can significantly improve circulation.
- Compression Therapy: Applying compression stockings or bandages can improve venous return and reduce swelling, particularly in cases of venous insufficiency. This technique is also effective in preventing deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Pharmacological Therapy: Prescribed medications, such as anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, or vasodilators, may be administered to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clots. These medications are carefully selected and monitored by the healthcare team.
- Oxygen Therapy: In cases of severe tissue hypoxia, supplemental oxygen therapy may be necessary to ensure adequate oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Education and Patient Empowerment: Emphasizing lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation, dietary changes, and regular exercise, is crucial. Nurses play a vital role in educating patients about their condition, promoting self-management, and empowering them to make informed decisions regarding their health.
Evaluation: Monitoring for Progress and Complications
The nursing care plan for impaired tissue perfusion is a dynamic process that requires ongoing evaluation. Nurses meticulously monitor the patient’s response to interventions, assessing changes in vital signs, skin color, temperature, and peripheral pulses. Early recognition of any deterioration in the patient’s condition is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of complications. Regular evaluation allows nurses to adjust the care plan, ensuring it remains effective and addresses the individualized needs of the patient.
Trends and Developments in Impaired Tissue Perfusion Management
The field of tissue perfusion management is constantly evolving, with advancements in medical technology and research leading to new and innovative approaches. Here are some significant trends and developments:
- Emerging Technologies: Novel diagnostic tools like Doppler ultrasound and laser Doppler flowmetry provide precise information about blood flow, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of impaired tissue perfusion. These advancements allow healthcare providers to make more informed clinical decisions.
- Personalized Medicine: With a growing understanding of the genetic and molecular basis of various diseases, personalized medicine offers the potential to tailor therapeutic interventions to individual patients, maximizing treatment effectiveness and minimizing side effects.
- Focus on Prevention: The importance of preventive strategies, such as early detection and management of risk factors for cardiovascular disease, is increasingly recognized. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, including regular exercise, balanced diet, and smoking cessation, plays a key role in preventing impaired tissue perfusion.
Tips and Expert Advice for Nursing Care
Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you provide excellent care to patients with impaired tissue perfusion:
- Pay Attention to the Details: Meticulously document changes in the patient’s condition, including any subtle alterations in vital signs, skin color, or pulse strength. This detailed documentation serves as a valuable reference for future care decisions and can help to identify early signs of deterioration.
- Collaborate Effectively: Open communication with the interdisciplinary team, including physicians, pharmacists, and physical therapists, is essential for coordinating and implementing the most effective care plan.
- Empower Your Patients: Educate patients about their condition, treatment options, and the importance of self-management. This empowers them to actively participate in their care and make informed decisions about their health.
Remember, effective nursing care involves not just managing the symptoms but also empowering patients to make informed choices that promote their overall well-being.
FAQs About Impaired Tissue Perfusion
Q: What are the major causes of impaired tissue perfusion?
A: The causes of impaired tissue perfusion are diverse and can include:
- Cardiovascular diseases: Heart attacks, coronary artery disease, heart failure
- Peripheral vascular diseases: Peripheral artery disease, deep vein thrombosis, varicose veins
- Trauma: Injury to blood vessels, such as lacerations or crush injuries
- Prolonged immobility: Reduced blood flow due to prolonged bed rest or inactivity
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels over time
- Smoking: Nicotine constricts blood vessels
- Certain medications: Some medications can have adverse effects on blood flow
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of impaired tissue perfusion?
A: The symptoms of impaired tissue perfusion can vary depending on the affected tissue and the severity of the condition. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Changes in skin color: Pallor, cyanosis (bluish discoloration), or redness
- Changes in skin temperature: Coldness or warmth to the touch
- Changes in peripheral pulses: Weak or absent pulses
- Edema: Swelling in the affected area
- Pain: Numbness, tingling, or burning sensation
- Altered sensation: Numbness or tingling
- Weak or absent motor function: Difficulty moving the affected limb
- Slow capillary refill: More than 2 seconds for color to return to the nail bed after pressure is applied
Q: How can I prevent impaired tissue perfusion?
A: Preventing impaired tissue perfusion involves adopting a healthy lifestyle:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Eat a balanced diet: Choose fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity helps improve blood flow and strengthens the heart.
- Quit smoking: Smoking significantly damages blood vessels and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Manage chronic conditions: Control diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
Impaired Tissue Perfusion Nursing Care Plan
Conclusion
Managing impaired tissue perfusion effectively requires a comprehensive approach involving accurate assessment, tailored interventions, and continuous evaluation. Nurses play a crucial role in this process, providing compassionate care and advocating for their patients. By understanding the intricacies of this condition and implementing evidence-based nursing practices, you can significantly improve the lives of patients experiencing impaired tissue perfusion. By embracing new technologies and fostering a culture of prevention, we can strive to create a world where impaired tissue perfusion is a manageable condition, not a life-limiting one.
Are you interested in learning more about impaired tissue perfusion or have any other questions related to this topic? If so, feel free to leave a comment below. I am always eager to engage in discussions and share my knowledge to enhance our collective understanding of this critical health issue.





