Imagine a world where the constant fear of fluctuating blood sugar levels, the daily burden of insulin injections, and the constant threat of complications associated with diabetes are things of the past. While this may seem like a distant dream, the reality is that with effective management and proactive nursing care, individuals living with diabetes can live fulfilling and healthy lives. This is where the NANDA nursing diabetes care plan comes in. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deep understanding of this powerful tool, enabling nurses and caregivers to better support those living with diabetes.
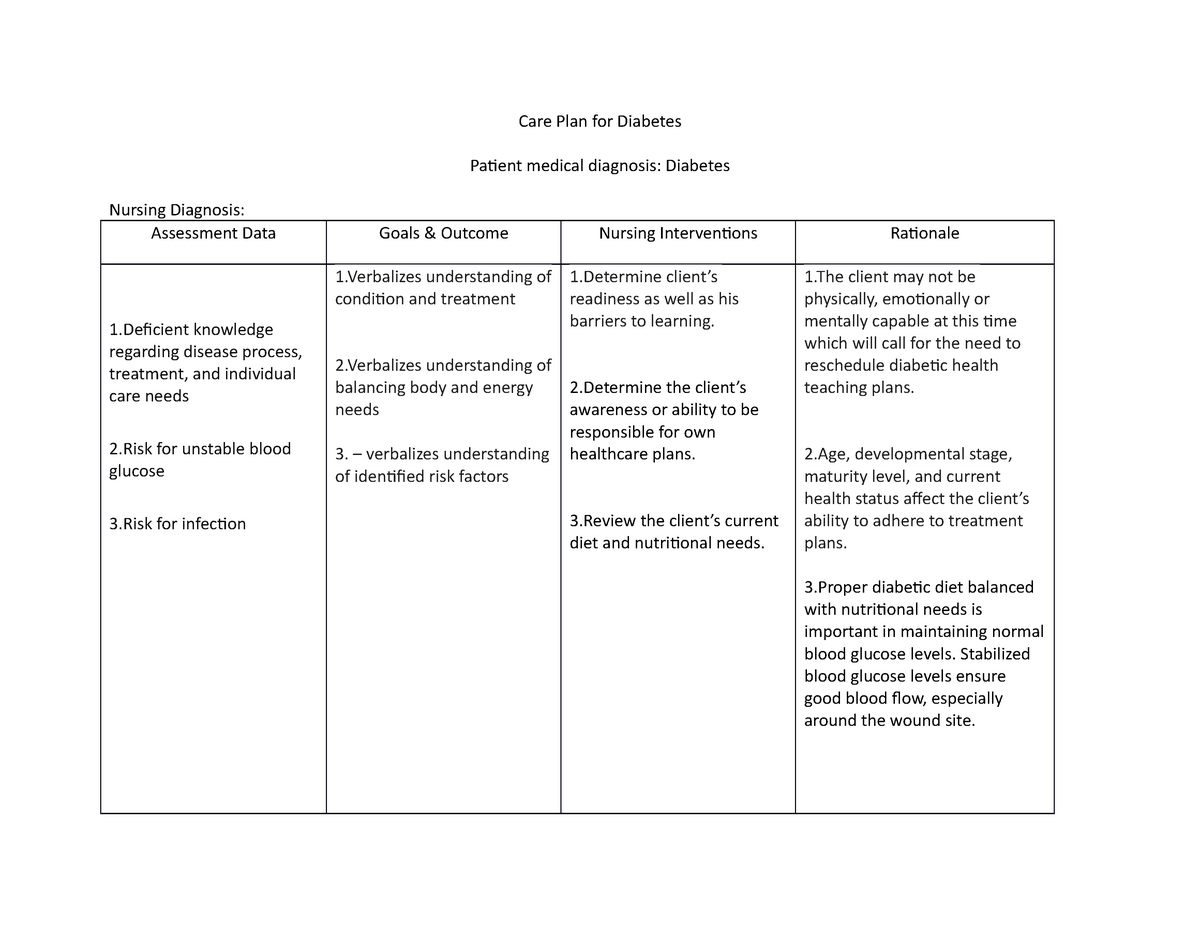
Image: www.studocu.com
The NANDA nursing diabetes care plan is a crucial resource that utilizes the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) standard nursing language. It’s a blueprint for providing personalized and individualized care to individuals with diabetes. By utilizing the NANDA framework, nurses can pinpoint the unique needs and challenges of each patient, developing a tailored care plan that addresses these individual concerns, promoting optimal health outcomes.
Understanding the NANDA Nursing Diabetes Care Plan
Defining the NANDA Nursing Diagnosis
The NANDA nursing diagnosis is the cornerstone of the nursing care plan. It’s a clinical judgment about an individual’s response to actual or potential health problems. In the context of diabetes, nurses use NANDA diagnoses to identify specific nursing concerns, including:
- Impaired Glucose Regulation: This diagnosis indicates an inability to maintain blood glucose levels within the desired range, potentially leading to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. This can stem from various factors, including lifestyle, medication, or underlying health conditions.
- Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose: This diagnosis identifies individuals at risk of unpredictable or erratic blood sugar fluctuations. This risk can be influenced by factors like inconsistent insulin administration, improper diet, or missed blood glucose monitoring.
- Ineffective Self-Management of Diabetes: This diagnosis reflects a patient’s difficulty in effectively managing their diabetes, potentially due to lack of knowledge, resources, or motivation. It can lead to poor adherence to the treatment plan and increased risk of complications.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Care Plan
The NANDA nursing diabetes care plan goes beyond simply diagnosing the condition. It serves as a roadmap, outlining the interventions and strategies designed to address the identified nursing diagnoses. This plan considers the patient’s individual needs, preferences, and goals, ultimately aiming to:
- Stabilize Blood Glucose Levels: Through individualized strategies, the care plan aims to maintain blood glucose levels within a safe and healthy range, reducing the risk of complications.
- Promote Self-Management Skills: Nurses play a vital role in educating patients on diabetes management, empowering them to actively participate in their care through diet, exercise, and medication adherence.
- Prevent Complications: The plan proactively addresses potential complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and foot problems, through early intervention and regular monitoring.
- Improve Quality of Life: More than just managing the disease, the NANDA nursing diabetes care plan aims to enhance the quality of life for individuals with diabetes, promoting their well-being and sense of control.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Essential Components of a NANDA Diabetes Care Plan
A comprehensive NANDA nursing diabetes care plan typically includes the following elements:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Assessment | This involves gathering information about the patient’s overall health, including their current blood glucose levels, medications, medical history, and lifestyle factors. It also includes patient interview and physical examinations. |
| Nursing Diagnosis | This is the identification of specific nursing concerns related to the patient’s diabetes, based on the gathered assessment information. Examples include impaired glucose regulation, risk for unstable blood glucose, and ineffective self-management of diabetes. |
| Planning | This involves setting realistic and measurable goals for the patient. Objectives should address minimizing risks and optimizing well-being. For example, aims can include achieving target blood sugar ranges, improving self-monitoring, or enhancing adherence to treatment regimens. |
| Interventions | These are the specific nursing actions aimed at achieving the established goals. They may include patient education, medication administration, blood glucose monitoring, nutritional counseling, exercise guidance, and communication with other healthcare providers. |
| Evaluation | This involves ongoing monitoring and assessment of the patient’s progress towards their goals. Regular evaluations are crucial for adapting the care plan, ensuring its effectiveness and making necessary adjustments as the patient’s needs change. |
Key Trends in Diabetes Care Planning
The field of diabetes care is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in research, technology, and an increased focus on patient empowerment. Here are some key trends shaping the way nurses approach diabetes care planning:
- Personalized Medicine: The focus is shifting towards tailoring treatment plans to each individual’s unique needs and genetic predispositions, emphasizing personalized diabetes management.
- Technology Integration: Technology is playing a critical role in supporting diabetes self-management. Devices like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, and smartphone apps empower patients to actively monitor and adjust their treatments.
- Improved Access to Resources: Increased awareness of diabetes, along with improved access to educational resources, support groups, and telehealth services, is empowering individuals with diabetes to actively participate in their care.
- Focus on Prevention: Efforts are focused on preventing type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modifications, such as healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management, particularly for individuals at risk.
Tips for Effective Diabetes Care Planning
Creating a successful NANDA nursing diabetes care plan requires a collaborative approach involving the patient, their family, and the healthcare team. Here are some expert tips to ensure the plan’s effectiveness:
- Engage the Patient: Involve the patient in every step of the care planning process, ensuring their needs, preferences, and goals are taken into account. This empowers them to actively participate in their care, increasing compliance and motivation.
- Employ Clear and Concise Language: Communicate the plan in language that is easy for the patient to understand. Avoid technical jargon and ensure the patient fully comprehends the rationale behind each intervention.
- Prioritize Self-Management Education: Equip the patient with the skills and knowledge to effectively manage their diabetes. Teach them about healthy lifestyle choices, meal planning, medication administration, and regular blood glucose monitoring.
- Facilitate Support Systems: Connect the patient with relevant support services, such as diabetes educators, registered dietitians, and support groups. This provides ongoing guidance, information, and emotional support.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage technology to enhance patient care and monitoring. Utilize smartphone apps for medication reminders, blood glucose tracking, and access to educational resources. Consider integrating continuous glucose monitors into the care plan.
Remember that effective diabetes care planning is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring, evaluation, and adjustments are crucial to ensure that the care plan remains relevant and effective in meeting the patient’s evolving needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a NANDA nursing diagnosis and a medical diagnosis?
A NANDA nursing diagnosis focuses on the patient’s response to actual or potential health problems, like their ability to manage their blood sugar or their risk for complications. In contrast, a medical diagnosis identifies a specific disease or condition, like diabetes itself.
Can I create my own NANDA diabetes care plan?
While you can have a basic understanding of your individual needs, creating a comprehensive NANDA nursing diabetes care plan requires specialized training and expertise. It is recommended to work closely with your healthcare providers, including nurses and doctors, to develop a personalized and effective plan.
How often should I review and update my NANDA diabetes care plan?
Your care plan should be reviewed and updated on a regular basis, at least annually, or more frequently if needed. Your healthcare provider will monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments according to your individual health status, changing lifestyle factors, and advancements in diabetes care.
Nanda Nursing Diabetes Care Plan Pdf
Conclusion
The NANDA nursing diabetes care plan is a crucial tool for providing effective and individualized support to individuals living with diabetes. By understanding its components, embracing key trends, and implementing best practices, nurses can significantly enhance the well-being and quality of life for those with this chronic condition. Remember, every individual with diabetes deserves a personalized care plan tailored to their unique needs.
Are you interested in learning more about NANDA nursing diabetes care plans or have questions about how to create one? Please share your thoughts in the comments below!





