Remember that moment when the lights suddenly went out, plunging your home into darkness? A chilling silence followed, leaving you scrambling for your phone to call an electrician. That feeling of helplessness is common, but it needn’t be. Learning the basics of home wiring empowers you to troubleshoot simple issues, understand your electrical system, and even undertake small wiring projects yourself. This step-by-step guide will take you from novice to confident DIYer, giving you the knowledge and skills to tackle home wiring with confidence and safety.

Image: guidefixjunker.z19.web.core.windows.net
Home wiring is the intricate network of cables and devices that brings electricity to your house. It’s the invisible backbone of modern life, powering everything from the lights in your living room to the appliances in your kitchen. Understanding how your home’s electrical system works is essential for maintaining a safe and functional living space. It empowers you to make informed decisions about your electrical needs, whether it’s adding a new outlet, upgrading your lighting, or installing a smart home system.
Diving into the World of Home Wiring: A Step-by-Step Guide
Before you grab your tools, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals of electrical safety. Electrical work can be hazardous if not done properly, so prioritize safety above all else. Always ensure the power is off to the circuit you’re working on, and use appropriate protective gear, such as insulated gloves and safety glasses. If you’re unsure about any aspect of home wiring, consult a qualified electrician.
1. Understanding Electrical Terminology
- Voltage (V): The force that pushes electrical current through a circuit. In homes, the standard voltage is 120V.
- Current (A): The flow of electrical charge through a circuit. Measured in amps (A).
- Resistance (Ω): The opposition to the flow of current, measured in ohms (Ω).
- Circuit: A closed loop path that electrical current follows.
- Breaker: A safety device that interrupts the flow of electricity if there’s an overload or short circuit.
2. Learning the Essentials of Wire Types and Sizes
- NM-B Cable (Romex): The most common type for residential wiring, consisting of two or more insulated conductors surrounded by a protective sheath.
- UF Cable (Underground Feeder): Designed for direct burial in the ground.
- THHN Wire: Used for individual runs of wire, often for appliances or specific circuits.
The size of wire, indicated by the gauge number, determines its current-carrying capacity. Larger gauge numbers signify smaller wire diameters, and vice versa. For example, 14-gauge wire is used for lights, while 12-gauge is used for outlets.
3. Exploring Different Electrical Components
- Outlets: Receptacles that provide power to devices by connecting to the electrical system.
- Switches: Devices that interrupt the flow of electricity to a circuit.
- Junction Boxes: Boxes where wires are connected, allowing for safe and organized wiring.
- Circuit Breakers: Safety devices in your electrical panel that protect circuits from overloads.
4. Basic Wiring Techniques for Simple Projects
- Splicing Wires: Connecting two wires together using wire connectors, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
- Terminating Wires: Connecting wires to terminals on outlets, switches, or other devices.
- Running Wires: Routing wires through walls, ceilings, or under floors, following specific safety guidelines.
5. Tackling Basic Home Wiring Projects
- Installing a Light Fixture: Connecting wires to the fixture and mounting it to a junction box.
- Adding an Outlet: Running a new wire from the electrical panel to the desired location and connecting it to the outlet.
- Replacing a Switch: Disconnect the power, remove the old switch, and install the new one, ensuring correct wire connections.
6. Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
- Dim Lights: Could be caused by a loose connection, a faulty bulb, or a problem with the circuit.
- Flickering Lights: May indicate a loose connection or a problem with the wiring.
- Tripped Circuit Breaker: Signifies an overload or short circuit, requiring investigation and repair.
Essential Tips from the Experts
- Never work on live circuits. Always disconnect power before working on any electrical components.
- Use appropriate tools: Invest in a good quality voltage tester, wire strippers, and a reliable electrical tool kit.
- Follow electrical codes: Adhering to national and local electrical codes ensures safety and proper installation.
- Consult a qualified electrician for complex projects: Don’t hesitate to call in a professional for major repairs or installations.
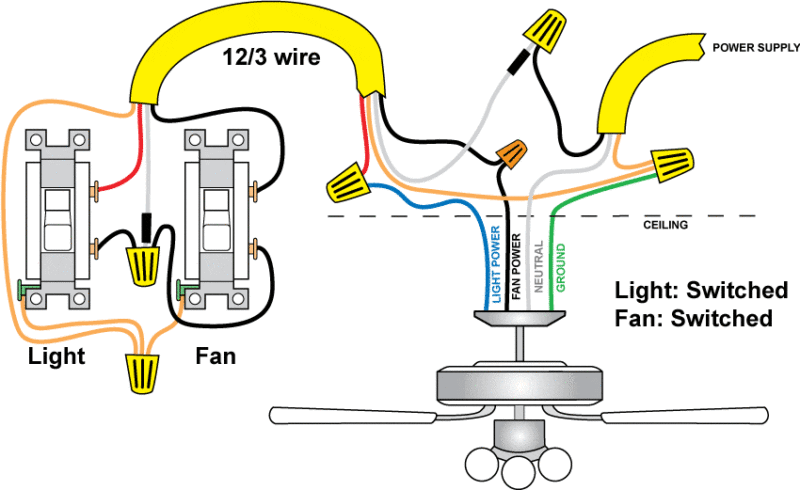
Image: shellysavonlea.net
Step By Step Guide Book Home Wiring
The Power of Empowerment: Embrace Your DIY Skills
Embracing the basics of home wiring empowers you to maintain a safe and functional living environment. By understanding the fundamental principles, learning essential techniques, and prioritizing safety, you can tackle simple home wiring projects with confidence. Remember, if you encounter a complex issue or are unsure, don’t hesitate to seek the guidance of a qualified electrician. This guide is just the beginning of your journey into the electrifying world of home wiring. The more you learn, the more you can empower yourself to manage your home’s electrical needs with efficiency and safety. Share your experiences, ask questions, and continue to explore this fascinating world of home wiring!





