Have you ever wondered how businesses keep track of their financial health? It all boils down to a simple yet powerful equation: the accounting equation. This foundational principle of accounting serves as the backbone for understanding financial statements and making informed business decisions. But navigating the world of debits, credits, and balance sheets can feel overwhelming, especially for beginners. Fear not! This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and resources to conquer the accounting equation with confidence, complete with a downloadable PDF containing practice questions and answers.
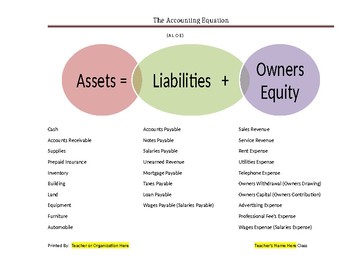
Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
In its simplest form, the accounting equation demonstrates the fundamental relationship between a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. It’s the cornerstone of double-entry bookkeeping, ensuring that every financial transaction is recorded in two separate accounts, maintaining a balanced equation. Understanding this equation unlocks a deeper comprehension of how businesses manage their finances, allowing you to analyze their performance and make informed decisions – whether you’re a student embarking on an accounting journey or a seasoned professional seeking a refresher.
Unveiling the Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is represented as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Let’s break down each component:
- Assets are resources owned or controlled by a company that are expected to provide future economic benefits. Examples include cash, inventory, accounts receivable, and equipment.
- Liabilities are obligations or debts owed to others. These represent claims against a company’s assets. Examples include accounts payable, loans, and salaries payable.
- Equity represents the shareholders’ ownership stake in a company. It reflects the value of the company remaining after liabilities are paid off. It’s often referred to as owner’s equity or shareholders’ equity.
Visualizing the Equation
Imagine a company is like a puzzle, with assets representing all the pieces. Liabilities are the pieces already claimed by others (like lenders or suppliers), and equity is what’s left for the owners.

Image: www.chegg.com
Understanding the Interplay
The accounting equation highlights the interconnectedness of these elements:
- Assets increase when a company acquires more resources or investments, often through borrowing (increasing liabilities) or generating profits (increasing equity).
- Assets decrease when a company uses resources or sells assets, potentially through paying off debts (decreasing liabilities) or distributing profits to owners (decreasing equity).
Applications of the Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is not just a theoretical concept; it plays a vital role in practical accounting tasks, including:
- Financial Statement Analysis: The accounting equation provides a framework for understanding the relationships between assets, liabilities, and equity, which are reflected in the balance sheet. This allows analysts to assess the financial health of a company.
- Transaction Recording: Every financial transaction is recorded in a way that maintains the equation’s balance. For example, if a company borrows money, it increases assets (cash) and also increases liabilities (loans payable).
- Decision-Making: Business leaders use the accounting equation to inform decisions regarding investments, pricing, and financing. By understanding the company’s financial position, they can make strategic decisions.
Common Accounting Equation Questions
Let’s dive into some frequently asked questions about the accounting equation:
1. What are the key elements of the accounting equation?
The three key elements are:
- Assets: Resources controlled by the company.
- Liabilities: Obligations owed to others.
- Equity: The owner’s interest in the company.
2. Why is the accounting equation important?
The accounting equation is important because it:
- Provides a framework for understanding financial statements.
- Ensures that every financial transaction is recorded accurately.
- Helps businesses make informed financial decisions.
3. How does the accounting equation relate to the balance sheet?
The balance sheet is a financial statement that presents a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. The accounting equation forms the basis for the balance sheet, as it shows the fundamental relationship between these elements.
4. How can I use the accounting equation to analyze a company’s financial performance?
By analyzing the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity, you can gain insights into a company’s financial health. For example, a high level of liabilities compared to equity might indicate a high level of risk, while a strong increase in assets might signal growth.
5. What are some examples of accounting equation transactions?
Here are a few examples:
- Borrowing money: Assets (cash) increase, and so do liabilities (loans payable).
- Purchasing equipment: Assets (equipment) increase, and assets (cash) decrease.
- Earning revenue: Assets (cash or accounts receivable) increase, and equity (retained earnings) increases.
- Paying dividends: Equity (retained earnings) decreases, and assets (cash) decrease.
Practice Makes Perfect: Download Your PDF Now!
Ready to put your knowledge to the test? We’ve compiled a comprehensive PDF with a variety of practice questions and answers covering the accounting equation. From identifying the elements to analyzing transactions, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of this essential concept. Download your copy today and embark on your journey to mastering the accounting equation!
Link to PDF download here
Accounting Equation Questions And Answers Pdf
Conclusion
Mastering the accounting equation is a crucial step in grasping the fundamental principles of accounting and financial analysis. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the equation, its components, applications, and common questions. We strongly encourage you to download our PDF and practice your newfound knowledge. With dedication and practice, you’ll gain confidence in navigating the financial world, making informed decisions, and achieving your financial goals.





