Imagine walking into a patient’s world, a world often shrouded in confusion and distress. You want to understand their experiences, their fears, their hopes—but how do you truly connect? In psychiatric nursing, the answer lies in a powerful tool: process recording. This meticulous documentation allows nurses to capture the intricate journey of their patients, unraveling the complexities of mental health and guiding them towards healing.

Image: www.scribd.com
Process recordings go beyond merely recording symptoms or medication details; they delve deeper into the patient’s narrative, capturing the interplay between their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This glimpse into the patient’s internal landscape empowers nurses to tailor care plans, fostering a stronger therapeutic relationship and ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Unveiling the Layers of a Process Recording
A process recording is like a diary, but a very specific one, meticulously structured to document the therapeutic encounter. It serves as a valuable tool for nurses, offering a platform to reflect on their interactions and identify patterns in their patient’s behavior. Let’s break down the key components of a process recording:
1. The Setting and the Participants
Every story begins with a setting. A process recording starts with a clear description of the environment where the interaction took place. Was it a quiet room, a bustling waiting area, or a walk in the park? Knowing the context provides valuable insight into the patient’s state of mind and the dynamics at play. The recording also identifies the participants involved, including the nurse, the patient, and any other individuals present.
2. The Interaction: A Tapestry of Words and Actions
The heart of the recording lies in the detailed account of the verbal and nonverbal communication between the nurse and the patient. Every word spoken, every gesture made, and every subtle shift in demeanor is documented. It might include:
- Direct Quotes: Capturing the exact words spoken by both the patient and the nurse, ensuring accuracy and preserving the essence of the exchange.
- Nonverbal Cues: Observations of the patient’s facial expressions, posture, body language, and tone of voice, offering a deeper understanding of their emotional state.
- Nurse’s Responses: Recording the nurse’s verbal and nonverbal actions, highlighting their therapeutic interventions, and evaluating their effectiveness.
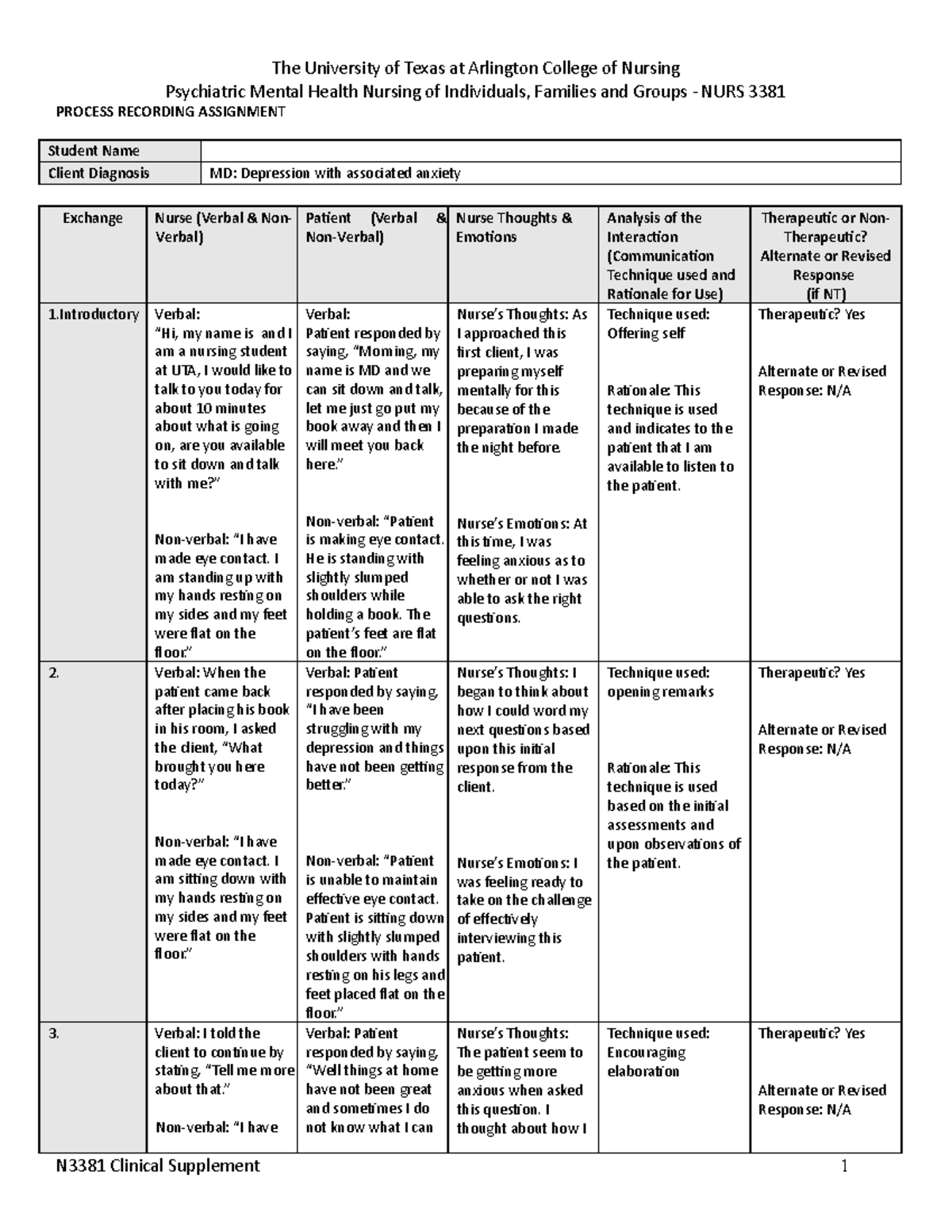
Image: www.studocu.com
3. The Nurse’s Observations and Reflections
This section offers a space for the nurse to analyze the interaction from a professional perspective. The nurse reflects on the patient’s emotional state, their communication patterns, and the impact of their own interventions. They might ask themselves questions like:
- What was the patient’s emotional state during the interaction? Were they anxious, depressed, agitated, or calm?
- What were the patient’s key concerns and motivations? What were they trying to communicate?
- How did the nurse’s actions influence the patient’s behavior? Did their interventions create a safe and supportive environment?
4. A Window into the Nurse’s Inner World
Beyond analyzing the patient, a process recording also allows the nurse to explore their own thoughts and feelings during the interaction. By recording their personal reactions, the nurse gains a deeper understanding of their own emotional responses and how they might impact their therapeutic approach.
- Countertransference: This involves exploring the nurse’s own reactions to the patient, recognizing if any personal experiences or biases are influencing their interactions.
- Self-Awareness: The recording prompts the nurse to reflect on their own emotional state and how it might affect their communication with the patient.
5. The Process Recording as a Learning Tool
The process recording goes beyond documentation – it fosters learning and growth. By meticulously reviewing their notes, nurses can:
- Identify patterns: Spot recurring themes in the patient’s communication, behavior, or emotional state.
- Evaluate interventions: Analyze the effectiveness of their therapeutic techniques and identify areas for improvement.
- Refine their therapeutic approach: Adapt their interventions based on their observations and reflections, tailoring care to meet the patient’s unique needs.
- Enhance self-awareness: Develop a deeper understanding of their own strengths, weaknesses, and emotional responses in therapeutic settings.
The Benefits of Process Recording
The benefits of process recording extend far beyond individual learning. It contributes to the wider field of psychiatric nursing by:
- Improving patient care: Enhanced understanding of patient needs leads to personalized interventions and improved outcomes.
- Strengthening therapeutic relationships: Nurses gain a deeper understanding of their patients, fostering trust and rapport.
- Fostering professional development: Process recordings serve as valuable learning tools, helping nurses refine their skills and approaches.
- Advancing the field: Data collected from process recordings can contribute to research and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Navigating the Complexities: Tips from Experts
While process recordings are incredibly valuable, successfully implementing them requires careful attention to detail and ethical considerations. Here are key tips from experts in the field:
- Confidentiality is paramount: Protecting patient privacy is crucial. Only authorized individuals should have access to these recordings, and all identifying information should be anonymized.
- Objectivity is key: Strive for neutrality in your observations and reflections. Avoid personal opinions or judgments that could bias your analysis.
- Transparency and feedback: Share your process recordings with your supervisors or colleagues for feedback and guidance. This collaborative approach helps refine your analysis and identify areas for improvement.
- Embrace continuous learning: Treat process recording as an ongoing process of reflection and growth. Regularly revisit your recordings, analyze your interventions, and adapt your approach based on your evolving understanding.
Sample Of Process Recording In Psychiatric Nursing
A Journey of Discovery, Healing, and Growth
Process recording is a powerful tool that empowers nurses to navigate the complex world of mental health. It allows them to delve deeper into the patient’s experience, fostering a stronger therapeutic relationship and guiding them towards healing and growth. By embracing this tool, nurses become partners in the journey of recovery, offering support, understanding, and hope in a world that can feel overwhelming and isolating.
If you are interested in learning more about process recordings or the field of psychiatric nursing, there are numerous resources available. Connect with your local psychiatric nursing association, explore online forums and communities, and seek out expert guidance to further your understanding and contribute to the advancement of mental health care.





