Imagine the joy of welcoming a new life into the world, a moment filled with love and anticipation. But for some mothers, this joyous occasion is tragically marred by a silent threat – postpartum hemorrhage. This potentially life-threatening condition can occur after childbirth, leaving mothers vulnerable and in dire need of expert care.
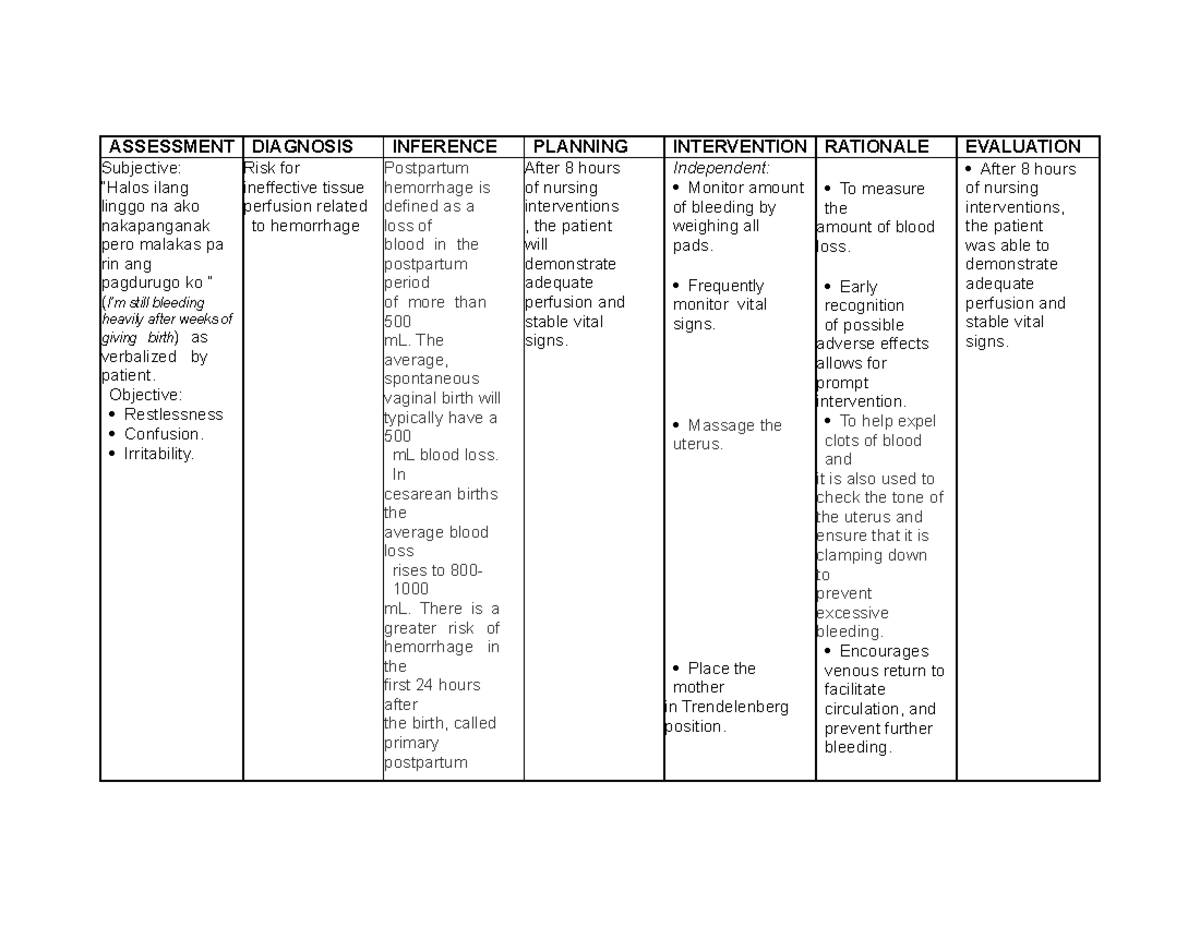
Image: www.studocu.com
Postpartum hemorrhage, defined as excessive bleeding after delivery, is a serious complication that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding its intricacies and developing effective nursing care plans is critical to ensuring the safety and well-being of mothers. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the complexities of postpartum hemorrhage, explore essential nursing interventions, and offer insights from leading experts to empower you with the knowledge to navigate this delicate situation.
Unveiling the Silent Threat: Understanding Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage, a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide, affects approximately 1 in 100 women who give birth. It can manifest in various forms, ranging from a gradual, persistent trickle to a sudden, massive outpour of blood. While the primary cause might be unclear in some cases, various factors contribute to its development, including:
- Uterine Atony: The most common cause, where the uterus fails to contract adequately after delivery, allowing continued bleeding.
- Lacerations: Tears in the cervix, vagina, or perineum can lead to significant blood loss.
- Retained Placenta: Incomplete expulsion of the placenta can obstruct the uterus, preventing proper contraction and leading to bleeding.
- Placenta Previa or Abruption: Abnormal positioning or detachment of the placenta can cause severe bleeding during or after delivery.
- Coagulation Disorders: Blood clotting disorders can hinder the body’s ability to stop bleeding.
A Lifesaving Blueprint: The Nursing Care Plan for Postpartum Hemorrhage
Faced with the urgency of a postpartum hemorrhage, nurses play a pivotal role in stabilizing the patient and preventing further complications. A comprehensive nursing care plan addresses multiple dimensions of the patient’s needs, from immediate interventions to long-term recovery support.
1. Assessment: The Cornerstone of Care
- Vital Signs: Continuous monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory rate reveals the severity of blood loss and the patient’s response to interventions.
- Fundal Assessment: Regular palpation of the uterus helps gauge its tone and identify any potential problems like uterine atony.
- Vaginal Examination: A careful examination helps identify lacerations or retained placental fragments.
- Blood Loss Estimation: Accurately estimating blood loss is crucial for guiding subsequent interventions and monitoring the patient’s condition.

Image: www.pinterest.co.uk
2. Early Interventions: Swift Action for Stability
- Uterine Massage: Gently massaging the fundus can stimulate contraction and reduce bleeding.
- Bimanual Compression: Applying pressure to the uterus internally and externally can help control bleeding.
- Fluid Resuscitation: Intravenous fluids are administered rapidly to replenish lost blood volume and maintain blood pressure.
- Blood Transfusions: If extensive blood loss occurs, blood transfusions are administered to restore vital blood components.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen is provided to enhance tissue oxygenation, particularly in cases of significant blood loss.
- Medication Administration: Uterine stimulants like oxytocin or methylergonovine are given to encourage uterine contractions and control bleeding.
3. Ongoing Monitoring and Support: Navigating the Recovery Journey
- Continuous Assessment: Vital signs, fundal height, and vaginal bleeding are meticulously monitored to assess the patient’s response to treatment.
- Pain Management: Analgesics are administered to manage uterine cramping and discomfort.
- Emotional Support: Providing emotional support and reassurance is crucial, as mothers may experience fear, anxiety, and distress during this critical time.
- Education and Discharge Planning: Educating patients about postpartum hemorrhage, its causes, and risk factors helps them understand their health better and empowers them to take proactive steps in future pregnancies.
- Referral to Specialists: If necessary, the nurse collaborates with specialists, such as obstetricians, hematologists, or anesthesiologists, for further evaluation and management.
Expertise Matters: Guiding Insights from Experienced Nurses
Experienced nurses emphasize the power of communication, collaboration, and unwavering vigilance in managing postpartum hemorrhage. They underline the importance of:
- Early Recognition: Quickly identifying potential signs of postpartum hemorrhage is crucial to initiating timely interventions.
- Teamwork: Working collaboratively with physicians, midwives, and other healthcare professionals ensures the patient receives a coordinated and comprehensive care approach.
- Patient-Centered Care: Understanding the patient’s individual needs and concerns helps create a supportive and empathetic environment.
Nursing Care Plan On Postpartum Hemorrhage
Empowering Yourself: A Call to Action
Postpartum hemorrhage is a complex medical condition requiring timely and effective intervention. Understanding its complexities, recognizing early signs, and knowing the essential nursing care plan components can be instrumental in ensuring the safety of mothers. Remember that every minute counts, and collaborative efforts by nurses and physicians are key to preventing catastrophic complications.
As we conclude this journey into the realm of postpartum hemorrhage, we urge you to cultivate awareness, seek comprehensive information, and advocate for improved maternal health outcomes. Stay informed, empower yourself, and join us in ensuring that motherhood is celebrated with safety and joy. If you have any concerns or questions, please consult a healthcare professional.





