Remember that frustrating moment in high school geometry when you couldn’t visualize the 3D shapes in your textbook? I certainly did. It felt like I was trying to decipher hieroglyphics, and I couldn’t grasp the concepts of volume and surface area. That was until I discovered the power of modeling geometric figures. Suddenly, geometry became less abstract and more tangible. Whether it’s building a model of a pyramid or carefully drawing a cube, the act of representing these shapes in a physical way unlocked a whole new level of understanding for me.
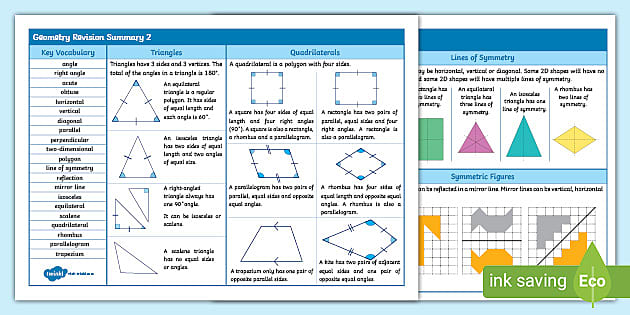
Image: www.twinkl.com.mx
It turns out that many students feel the same way. Modeling geometric figures is a valuable strategy for students of all ages, and it’s especially important for those taking geometry quizzes. This module, often dubbed “Module D,” is designed to test students’ ability to apply their knowledge of geometric concepts to real-world scenarios, and the best way to prepare for this is by getting hands-on with the shapes themselves. Let’s delve into the world of geometric modeling and explore how it can help you ace that next quiz.
Understanding Geometric Modeling: More Than Just Playing with Shapes
Geometric modeling doesn’t just involve building a cute house out of cardboard. It’s a dynamic process that requires students to think critically about the relationships between different geometric figures and how they can be transformed into 2D or 3D representations. At its core, it’s about bridging the gap between abstract geometric concepts and the physical world, something that can be particularly helpful when tackling complex problems like finding the volume of a cone or the surface area of a sphere.
Many students find geometric modeling to be an engaging and effective way to learn. It allows them to visually manipulate shapes, experiment with different properties, and develop a deeper understanding of geometric principles. It’s not just about building the model itself; it’s about the questions that arise during the process. Why does a cube have six equal sides? How can you change the dimensions of a cone to increase its volume? These are the sorts of questions that get students thinking critically and applying their knowledge to real-world situations.
The Building Blocks of Geometric Modeling: A Deep Dive into the Basics
At the heart of geometric modeling is understanding the key elements of geometry. This includes:
- **Points, lines, and planes:** These are the fundamental building blocks of geometry. Points mark locations in space, lines connect points, and planes are flat surfaces that extend infinitely.
- **Angles and their properties:** Angles are formed when two lines intersect. Learning about different types of angles, such as acute, obtuse, and right angles, is essential for understanding geometric shapes.
- **Polygons and their classifications:** Polygons are closed figures made up of straight line segments. Understanding the different types of polygons, such as triangles, squares, and pentagons, is crucial for analyzing and modeling 2D shapes.
- **Solids and their properties:** Solids are three-dimensional objects that have volume. This includes prisms, cubes, cylinders, and spheres. Knowing about their properties, like surface area and volume, is critical for geometric modeling.
- **Transformations: Translations, Rotations, and Reflections:** These operations allow us to move geometric figures around in space. Understanding how transformations affect shapes is vital for creating and manipulating models.
By mastering these concepts, students can effectively model geometric figures with accuracy and precision. This foundation sets the stage for tackling complex constructions and solving intricate geometric problems.
Mastering Geometric Modeling: Techniques and Tools for Success
Effective geometric modeling requires both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Let’s explore some key techniques and tools that can empower students to achieve mastery:

Image: www.coursehero.com
Hands-On Activities
- Construction paper modeling: This classic method lets students cut, fold, and assemble basic shapes to visualize their properties.
- Lego building: The modular nature of Lego bricks allows students to experiment with spatial relationships and create intricate structures.
- 3D printing: This cutting-edge technology allows students to design and print real-life models of geometric figures, promoting deeper understanding and creativity.
Digital Tools
- Geometry software programs: Programs like GeoGebra and SketchUp provide interactive platforms for creating and manipulating geometric shapes, offering a dynamic learning experience.
- Virtual reality (VR) simulations: VR environments can immerse students in a 3D world, allowing them to explore and interact with geometric figures from a new perspective.
By combining hands-on activities with digital tools, students can engage with geometry in a multi-sensory and engaging manner. This approach fosters deeper understanding and enhances their ability to solve problems effectively.
Leveraging Geometric Modeling to Ace Module D
As mentioned earlier, the “Modeling Geometric Figures” module, often labeled as Module D in various educational curriculums, is designed to assess students’ ability to apply their geometric knowledge to real-world problems. By using geometric modeling techniques, students can gain a competitive edge on this critical module.
Here are some tips to effectively prepare:
- Practice modeling different geometric figures: Go beyond the basics. Try to construct more complex shapes like pyramids, cones, and even compound figures. This hands-on practice helps build your spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills.
- Analyze real-world examples: Look around your environment for examples of geometric shapes. Identify different types of polygons in buildings, or observe spherical objects in your surroundings. This helps bridge the gap between abstract concepts and real-world applications.
- Work through practice problems: Module D often involves scenario-based questions. Practice solving these problems using your modeling skills to develop your strategic thinking and analytical abilities.
By implementing these strategies and developing an appreciation for geometric modeling, students can approach the challenge of Module D with confidence and achieve a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Remember, the key to success lies in actively engaging with the material and utilizing diverse learning methods.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions about Geometric Modeling
Here are some frequently asked questions about geometric modeling and how it relates to Module D.
Q: What are some common mistakes students make when modeling geometric figures?
A: Some common mistakes include:
- Not understanding the basic properties of shapes: For example, confusing the formula for volume with surface area.
- Failing to visualize the 3D shape from a 2D drawing: This is where practice and hands-on modeling come in.
- Not paying attention to scale and proportion: Accurate geometric modeling requires understanding how the dimensions of shapes relate to each other.
Q: Is it better to use hands-on modeling or digital tools?
A: Both hands-on modeling and digital tools are valuable. Hands-on modeling is great for developing spatial awareness, while digital tools offer more precision and flexibility. The ideal approach is to combine both methods.
Q: Are there any online resources to help me learn more about geometric modeling?
A: Absolutely! There are many great websites and online learning platforms dedicated to geometric modeling. Check out:
- Khan Academy: This platform offers a wealth of free resources, including video lessons and practice exercises for various geometric concepts.
- GeoGebra: A fantastic interactive geometry software that allows students to create and explore geometric figures.
- YouTube: Many educators share helpful tutorials and demonstrations online, making it easy to find instructions on specific modeling techniques.
Modeling Geometric Figures Module Quiz D
Conclusion: Master the Geometry Module with Confidence
By embracing geometric modeling and utilizing the tips and resources outlined in this article, students can develop a solid understanding of geometry and confidently tackle the challenges presented within Module D. Remember, the key is to experiment, explore different models, and engage in active learning. It’s not just about memorizing formulas; it’s about developing a deep understanding of the principles that govern the shapes that surround us.
Are you ready to build your geometric modeling skills and conquer Module D? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!





