Have you ever wondered what makes up everything around us? From the air we breathe to the chair you’re sitting on, it all boils down to one fundamental concept: matter. But what exactly is matter, and how can we understand the different forms it takes? This study guide is your key to unlocking the fascinating world of matter, exploring its properties, classifications, and the scientific principles that govern how it behaves.
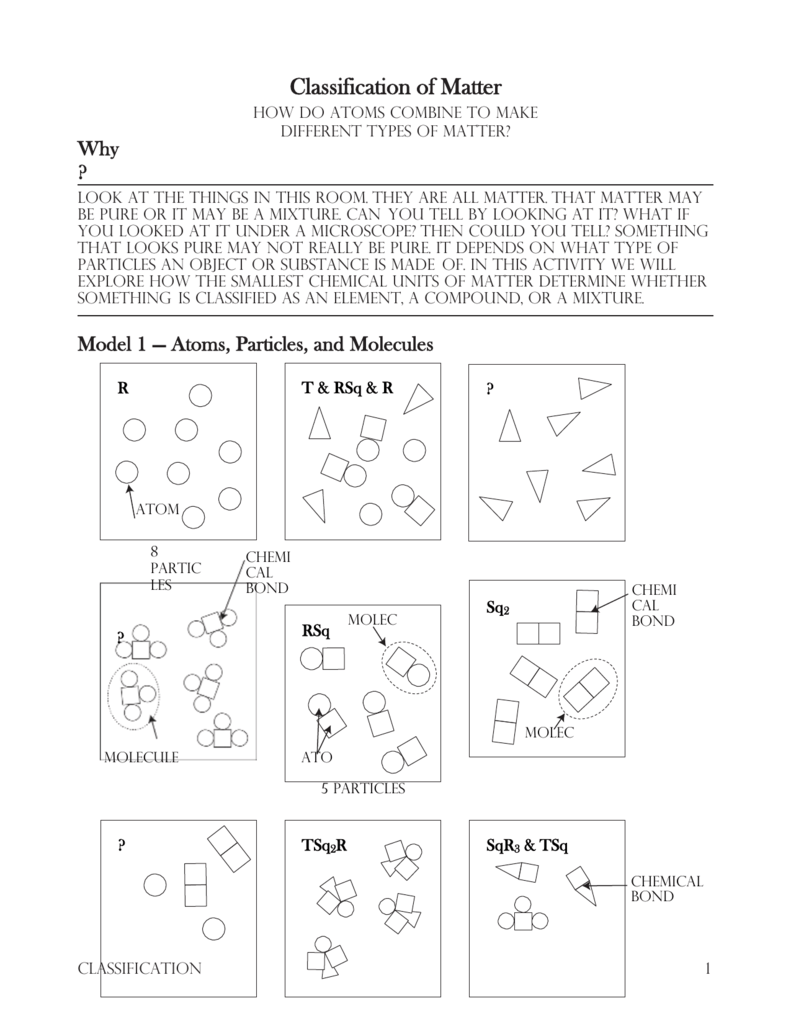
Image: eqlknkywby.blogspot.com
This first unit in your matter study guide serves as a foundation for understanding the physical world around us. It will guide you through defining matter, exploring its states of existence, and delving into the composition and structure of matter. You will learn about the different types of matter and how scientists classify them. By the end of this unit, you’ll have a solid grasp of the fundamental concepts of matter, enabling you to apply this knowledge to more advanced scientific explorations.
What is Matter?
At its simplest definition, matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while the space an object occupies is its volume. From a tiny atom to a massive star, anything that possesses these two characteristics is considered matter.
Examples of Matter
- Solid: A rock, a book, a table, a tree
- Liquid: Water, juice, oil, mercury
- Gas: Air, oxygen, helium, carbon dioxide
- Plasma: The sun, lightning, fluorescent lights
States of Matter
Matter exists in various states, each defined by its unique properties:
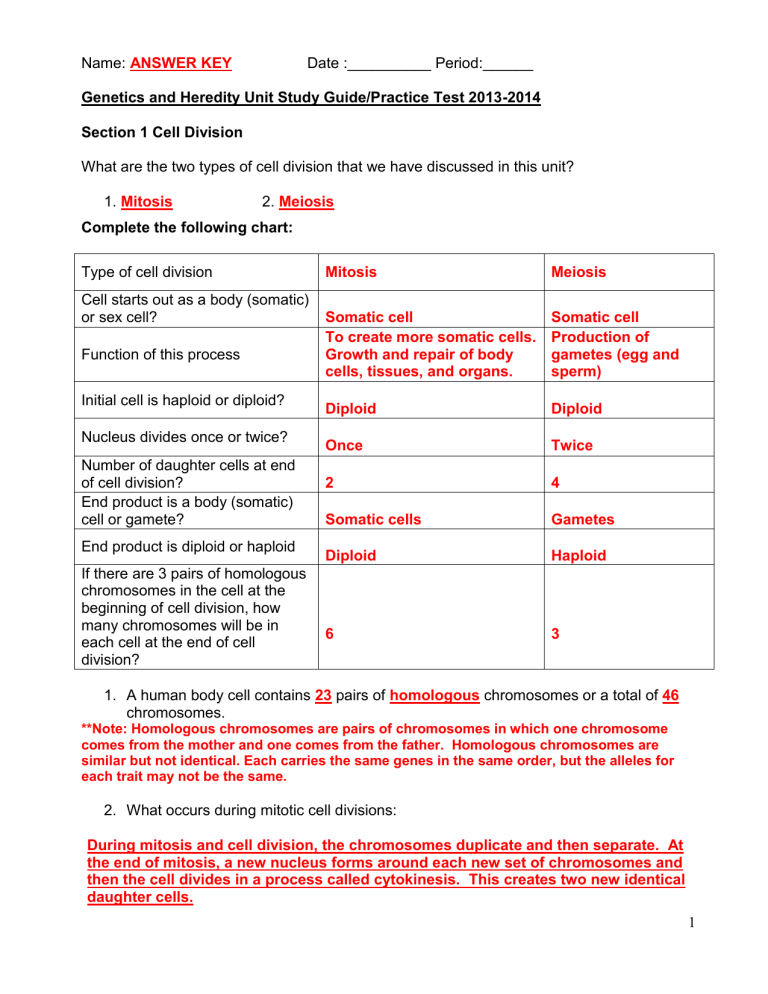
Image: studylib.net
Solid
- Fixed shape: Solids maintain a definite shape, resisting changes in form.
- Fixed volume: Solids have a specific volume that does not easily change.
- Closely packed particles: The particles in solids are tightly packed, arranged in a regular structure.
- Low compressibility: Solids are difficult to compress due to the close proximity of their particles.
Liquid
- Variable shape: Liquids take the shape of their container.
- Fixed volume: Liquids maintain a constant volume even when poured into different containers.
- Closely packed particles but mobile: Liquid particles are closely packed but have more freedom to move around.
- Moderate compressibility: Liquids can be compressed to some degree.
Gas
- Variable shape: Gases take the shape of their container.
- Variable volume: Gases can expand or contract to fill any container they occupy.
- Widely spaced particles: Gas particles are far apart and move freely.
- Highly compressible: Gases are easily compressed due to the large spaces between their particles.
Plasma
- Ionized particles: Plasma is a superheated gas containing free ions and electrons.
- High energy: Plasma requires extremely high temperatures to form.
- Conductive: Plasma conducts electricity and magnetic fields.
The Composition of Matter
Matter is not just a uniform substance but is made up of smaller, fundamental units called **atoms**. Atoms are the building blocks of all matter, and they are incredibly tiny. Each element in the periodic table is defined by a specific type of atom. For example, all gold atoms are identical to each other, and they are different from atoms of silver or copper.
Elements and Compounds
- Elements: Pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. Examples include gold, silver, oxygen, hydrogen
- Compounds: Substances formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. For instance, water (H2O) is a compound composed of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
- Mixtures: Combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. Examples include sand and water, air (a mixture of gases), and saltwater.
Understanding Matter’s Properties
The observable characteristics of matter are crucial for understanding its behavior. These properties can be classified as either **physical** or **chemical**:
Physical Properties
- Color: The way matter appears to the human eye.
- Density: The amount of mass per unit volume of a substance.
- Melting point: The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid.
- Boiling point: The temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas.
- Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance.
- Conductivity: The ability of a substance to conduct heat or electricity.
Chemical Properties
- Flammability: The ability of a substance to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Reactivity: The tendency of a substance to undergo chemical reactions.
- Corrosion: The gradual deterioration of a substance due to chemical reactions with its environment.
- Combustibility: The ability of a substance to react with oxygen to produce heat and light.
The Importance of Understanding Matter
Understanding the nature of matter is essential for numerous reasons:
- Technological advancements: Our ability to design and invent new materials and technologies depends on our knowledge of matter’s properties and behavior.
- Environmental protection: Understanding the impact of matter on the environment helps us develop sustainable practices and reduce pollution.
- Medical discoveries: Understanding matter at the atomic and molecular level is crucial for developing new medicines and treatments.
- Everyday life: Our daily experiences from cooking to cleaning involve interactions with matter.
Further Exploration
This study guide provides a foundational understanding of matter. As you progress in your science studies, you will delve deeper into the intricacies of atomic structure, chemical bonding, and the fascinating world of materials science. Remember, the journey of understanding matter is an ongoing one, and the more you explore, the more you’ll discover about the wonders of the physical world around us.
Matter Unit Study Guide 1 Answer Key
Key Takeaways
- Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It exists in different states: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
- Matter is composed of atoms, which are the fundamental building blocks of all substances.
- Elements are pure substances made of one type of atom, while compounds are formed by chemical combinations of two or more elements.
- Understanding matter’s properties, both physical and chemical, is crucial for technological advancements, environmental protection, and our daily lives.
- This study guide serves as a stepping stone on your journey to discovering the fascinating world of matter. There is always more to learn and explore!





