Have you ever felt compelled to wash your hands repeatedly, even after they’re already clean? Or maybe you find yourself arranging items in a specific order, feeling uneasy if they’re even slightly out of place? These are just two examples of the many ways obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can manifest in individuals. While many people experience occasional intrusive thoughts or compulsions, OCD is a chronic mental health condition that can significantly impact a person’s daily life.
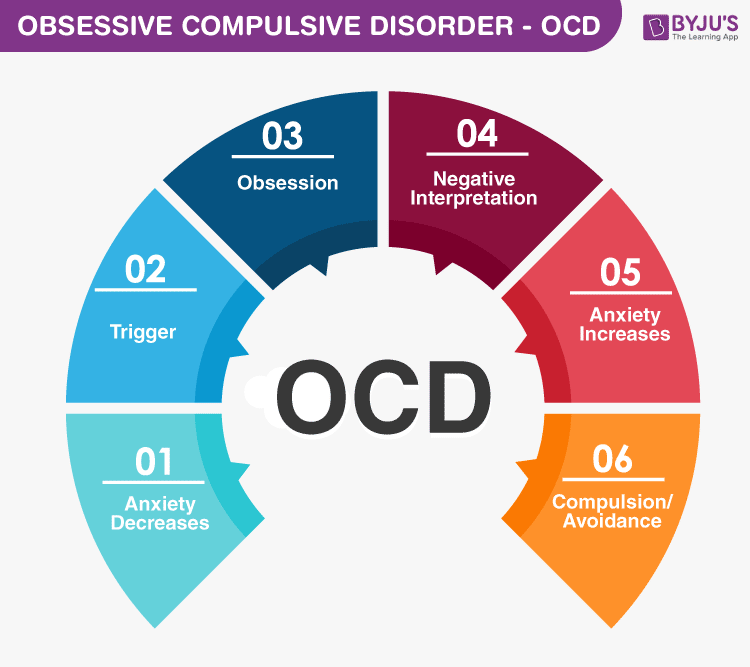
Image: drsamyaktiwari.com
Understanding how OCD manifests itself and how it impacts individuals is crucial for nurses. As healthcare professionals, nurses are often the first point of contact for patients seeking help. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of OCD, nurses can provide essential support and guidance. This article delves into the world of nursing diagnosis for OCD, exploring the unique challenges this condition presents and how nurses can effectively assist those living with it.
Understanding Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). These obsessions and compulsions can range from seemingly harmless to debilitating, often consuming vast amounts of time and energy and hindering an individual’s ability to function in their daily life.
Obsessions are recurring and intrusive thoughts, images, or urges that cause intense anxiety and distress. They are often unwanted and perceived as irrational by the individual, yet they can be incredibly difficult to control or ignore. Compulsions, on the other hand, are repetitive behaviors or mental acts that individuals perform in an attempt to reduce the anxiety associated with their obsessions. These behaviors can include actions like excessive hand washing, repeatedly checking locks, or ordering and arranging objects in a specific way.
Types of Obsessions
The content of obsessions can vary greatly from person to person, but some common themes include:
- Contamination fears: A fear of contamination by germs, dirt, or other substances, leading to excessive hand washing, cleaning, or avoidance of contact with certain objects.
- Harm obsessions: Fears of causing harm to oneself or others, leading to compulsions like checking locks, appliances, or repeatedly asking for reassurance.
- Symmetry and order obsessions: A need for things to be symmetrical, perfectly aligned, or arranged in a particular order, leading to repetitive actions like rearranging items or adjusting objects.
- Religious or moral obsessions: Concerns about religious or moral transgressions, leading to rituals or compulsions aimed at seeking forgiveness or atonement.
- Sexual obsessions: Unwanted and intrusive sexual thoughts or images that are disturbing or distressing.
Types of Compulsions
Compulsions are behaviors or mental acts that individuals engage in to alleviate anxiety associated with their obsessions. These behaviors can include:
- Washing: Excessive hand washing, showering, or cleaning.
- Checking: Repeatedly checking locks, appliances, or other things to ensure they are safe or in order.
- Repeating: Performing certain actions, like counting, saying words, or doing routines, a specific number of times.
- Ordering and arranging: Needing to arrange objects in a specific way, aligning them symmetrically, or maintaining order.
- Mental rituals: Performing mental acts like counting, reciting prayers, or repeating phrases to reduce anxiety.

Image: www.researchgate.net
Nursing Diagnoses for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Nurses play a vital role in the assessment, diagnosis, and care of individuals with OCD. It’s important for nurses to have a solid understanding of the common nursing diagnoses associated with this condition. Here are some of the most common nursing diagnoses for OCD:
1. Anxiety
Anxiety is a central feature of OCD, as individuals often experience significant distress due to their obsessions and compulsions. This diagnosis would be relevant if the patient exhibits symptoms such as:
- Restlessness or feeling keyed up
- Difficulty concentrating
- Muscle tension
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Increased heart rate
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling overwhelmed
2. Ineffective Coping
Individuals with OCD may struggle with coping mechanisms that effectively manage their anxiety and distress. This diagnosis is applicable when a patient exhibits behaviors like:
- Using unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as substance abuse or avoidance
- Experiencing difficulty managing stress
- Engaging in behaviors that exacerbate their OCD symptoms
- Having a limited range of coping strategies
3. Disturbed Sleep Pattern
OCD can significantly impact sleep quality, as anxiety and intrusive thoughts can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. This diagnosis would be appropriate if a patient reports:
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Waking up frequently during the night
- Early morning awakenings
- Feeling tired or exhausted during the day
- Experiencing nightmares or vivid dreams
4. Impaired Social Interaction
OCD can lead to social isolation and difficulty engaging in social situations, as individuals may avoid activities that trigger their OCD symptoms or fear being judged by others. This diagnosis is relevant if a patient exhibits:
- Social withdrawal
- Limited social contact
- Difficulty expressing feelings
- Fear of social situations
- Avoidance of social interactions
5. Self-Care Deficit
OCD can consume a significant amount of time and energy, interfering with basic self-care activities. This diagnosis is applicable if a patient reports:
- Neglecting personal hygiene
- Failing to meet basic nutritional needs
- Skipping meals or eating excessively
- Not engaging in regular exercise
- Having difficulty managing daily tasks
Nursing Interventions for OCD
Nursing interventions for OCD are designed to address the underlying causes of the condition and help individuals manage their symptoms. Some common nursing interventions include:
1. Providing Psychoeducation
Educating patients about OCD is essential for improving their understanding of the condition and reducing feelings of shame or stigma. Nurses can provide information about:
- The nature of OCD and its symptoms
- The neurobiological basis of OCD
- The importance of treatment adherence
- The role of therapy and medication
- Available support resources
2. Promoting Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can help reduce anxiety and tension, offering a valuable tool for managing OCD symptoms. Nurses can teach patients various techniques, such as:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Meditation or mindfulness techniques
- Yoga or tai chi
3. Facilitate Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a highly effective treatment for OCD, helping individuals identify and challenge their negative thoughts and behaviors. Nurses can:
- Refer patients to qualified mental health professionals for CBT
- Provide support and encouragement during the therapy process
- Assist patients in identifying and implementing CBT techniques in their daily life
4. Assist with Medication Management
Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can be helpful in reducing OCD symptoms. Nurses play a crucial role in:
- Monitoring medication effectiveness
- Observing for potential side effects
- Providing education about medication management
- Encouraging patients to adhere to their prescribed medication regimen
5. Create a Safe and Supportive Environment
Creating a safe and supportive environment is essential for patients experiencing OCD. Nurses can contribute by:
- Providing a calming and non-judgmental atmosphere
- Listening attentively to patients’ concerns
- Validating patients’ feelings and experiences
- Encouraging open communication and collaboration
6. Encourage Engagement in Activities
Encouraging patients to participate in activities they enjoy can help them regain a sense of control and improve their quality of life. Nurses can:
- Identify activities that interest patients
- Encourage social engagement through support groups or other activities
- Assist patients in developing a schedule that includes leisure activities
7. Promote Self-Care
Assisting patients in prioritizing self-care is essential for managing OCD symptoms and improving overall well-being. Nurses can:
- Encourage patients to eat a balanced diet
- Promote regular exercise
- Stress the importance of adequate sleep
- Help patients develop a self-care routine that they can maintain
Nursing Diagnosis For Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Conclusion
Nursing diagnosis for obsessive-compulsive disorder is a critical aspect of providing comprehensive care to individuals with this challenging condition. By understanding the unique challenges that OCD presents, nurses can effectively recognize, assess, and intervene to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. Nurses can be invaluable allies for those living with OCD, offering support, guidance, and resources to navigate this complex disorder. If you’re struggling with OCD, remember that you are not alone. Seek support from a qualified mental health professional and explore the resources available to you. Remember, recovery is possible, and hope is always within reach.





