As a tech enthusiast, I’ve always been fascinated by the constant evolution of processors, especially Intel’s. From the early days of the Pentium to the latest Core i9 series, Intel has consistently pushed the boundaries of performance. But navigating the different generations and their features can feel overwhelming. That’s why I’ve put together this guide to help you understand Intel processors better.
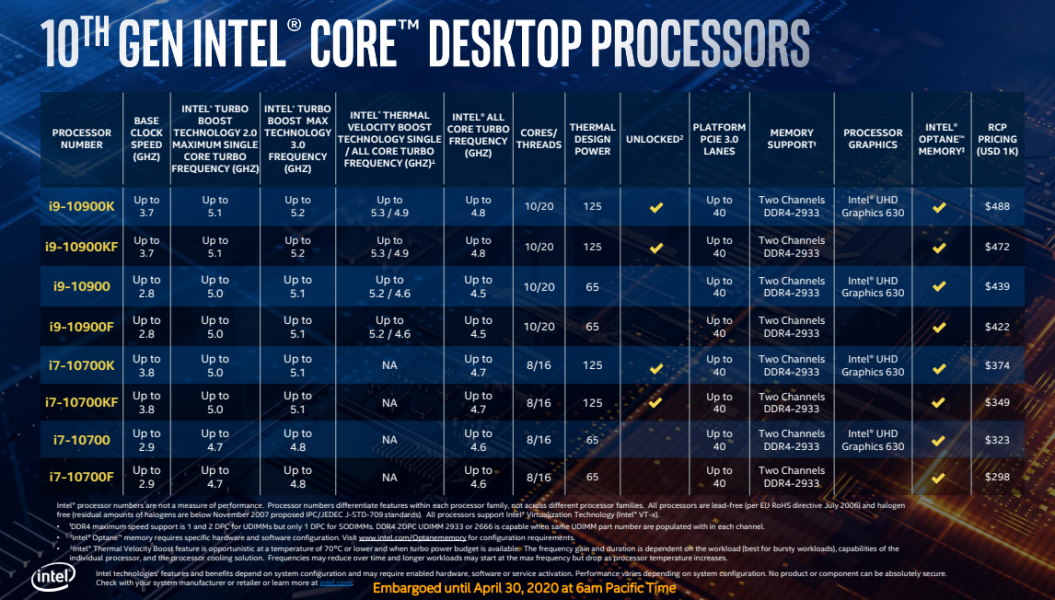
Image: www.lowyat.net
This guide is your one-stop resource for a comprehensive overview of Intel processors, from their history and architecture to their performance characteristics and compatibility. Whether you’re a seasoned techie or just starting to explore the world of CPUs, this list of Intel processors by generation in PDF format will guide you through the complexities of Intel’s processor evolution.
Understanding Intel Processor Generations
Intel processor generations represent a chronological progression of technological advancements, each bringing significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and features. Intel typically releases a new generation every 1-2 years, incorporating new architectures, fabrication processes, and enhancements to deliver greater processing power.
To understand the generations better, think of them as families. Each generation has a unique name (e.g., Pentium, Celeron, Core i3, i5, i7, i9) and comprises various models with differing core counts, clock speeds, and cache sizes. This means that within a single generation, you’ll find different Intel processors suited for various tasks and budgets.
A Detailed Breakdown of Intel Processor Generations
1st Generation Intel Processors (1993 – 2000):
This generation laid the foundation with the introduction of the iconic Pentium brand, offering a significant leap in performance over previous processors. The Pentium processor family offered a notable leap in performance over earlier generations. This was the first time Intel utilized a superscalar architecture, enabling multiple instructions to execute simultaneously. Popular models included the Pentium 75 and 133 MHz.

Image: skpdf.com
2nd Generation Intel Processors (2000 – 2006):
The 2nd generation marked the arrival of the Pentium III and Pentium 4, introducing advancements like the introduction of the SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) instruction set enhancing multimedia performance. The Pentium 4 was the first to incorporate hyper-threading technology, enabling a single core to handle multiple threads simultaneously, boosting application efficiency.
3rd Generation Intel Processors (2006 – 2010):
This generation witnessed the introduction of the Core architecture, a major shift in Intel’s processor design. It featured a more power-efficient design and introduced the Core 2 Duo and Core 2 Quad series. The Core 2 Duo introduced dual-core processors, paving the way for multi-core systems. Popular models included the Core 2 Duo E6400 and E8400.
4th Generation Intel Processors (2010 – 2013):
The 4th generation marked the arrival of the Sandy Bridge architecture, delivering significant performance improvements. It introduced Intel’s integrated graphics (Intel HD Graphics) and support for DDR3 memory. This generation included the Core i3, i5, and i7 series featuring models like the Core i7-2600K.
5th Generation Intel Processors (2013 – 2015):
This generation, commonly known as Haswell, concentrated on optimizing power efficiency and increasing performance while lowering power consumption. This generation featured the updated Core i3, i5, and i7 series with models like the Core i7-4770K.
6th Generation Intel Processors (2015 – 2017):
Known as Skylake, the 6th generation introduced improvements in graphics performance and introduced PCIe 3.0 support. This generation introduced the Core i3, i5, and i7 series with models like the Core i7-6700K.
7th Generation Intel Processors (2017 – 2019):
Kaby Lake offered minor performance improvements from the previous generation. The 7th generation included the Core i3, i5, and i7 series with models like the Core i7-7700K.
8th Generation Intel Processors (2018 – 2020):
Coffee Lake introduced a significant change, going from 4 to 6 cores on the mainstream Core i5 series. Performance improvements were considerable. The 8th generation contained the Core i3, i5, and i7 series with models like the Core i7-8700K.
9th Generation Intel Processors (2019 – 2020):
This generation, known as Coffee Lake Refresh, featured a small performance increase and improvements to the integrated graphics. It introduced the Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 series with models like the Core i9-9900K.
10th Generation Intel Processors (2020 – 2022):
Comet Lake included a slight improvement to the base clock speeds and the number of cores. This generation featured the Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 series with models like the Core i9-10900K. It also introduced the first “S” series mobile CPUs designed for ultra-thin laptops.
11th Generation Intel Processors (2021 – 2022):
Rocket Lake-S is known for its improved performance and the addition of Thunderbolt 4 support. This generation featured the Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 series with models like the Core i9-11900K.
12th Generation Intel Processors (2021 – Present)
Alder Lake was a game-changer for Intel, introducing the hybrid architecture with Performance (P) and Efficient (E) cores. This design significantly improved power consumption without sacrificing performance. It included Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 series, with popular models like the Core i9-12900K. This generation also introduced DDR5 memory support!
13th Generation Intel Processors (2022 – Present)
Raptor Lake is an evolution of Alder Lake, pushing the bounds further. The 13th generation features improved performance and efficiency, with enhanced P and E cores. It also includes new features like built-in AI acceleration and enhanced integrated graphics. This generation included Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 series, with popular models like the Core i9-13900K.
Intel Processor List by Generation PDF: Navigating and Using the PDF
To help you get the most out of this resource, the Intel processor list by generation PDF is organized for clarity and ease of use. It provides a detailed overview of each generation, including key advancements, major model releases (including laptop and desktop CPUs), and supporting technology. The PDF also offers additional insights into thermal design power (TDP) ratings, core counts, frequencies, compatible chipsets, and more. The PDF is also designed for easy navigation, with each generation clearly labeled and categorized for quick reference.
Expert Tips for Understanding Intel Processors
Navigating the world of Intel processors can be overwhelming, especially with each generation bringing new features and terminologies. Here are some tips to help you make informed decisions:
1. Performance vs. Power Consumption:
Consider your usage. If high-end gaming and professional applications are your priority, prioritize performance and opt for a processor with a higher core count and clock speed. If you’re primarily focused on basic tasks and everyday computing, look for a more power-efficient processor to maximize battery life.
2. Focus on the Core i Series:
The Core i3, i5, and i7 series cater to various needs. The Core i3 typically offers entry-level performance, while the Core i5 provides a balanced blend of performance and power efficiency. The Core i7, often found in high-end systems, delivers top-of-the-line performance.
3. Check for Compatibility:
Ensure that the processor you choose is compatible with your motherboard’s socket type. Intel has various socket types, each compatible with specific processors. Consult the motherboard’s specifications or Intel’s website for information.
4. Don’t Forget Integrated Graphics:
Many Intel processors come with integrated graphics, eliminating the need for a separate graphics card for basic computing. Integrated graphics can handle basic tasks like web browsing and video playback. However, for demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, a dedicated graphics card is recommended.
FAQs on Intel Processors
Here are some frequently asked questions about Intel processors:
Q: What is the difference between Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processors?
A: Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processors are designed for various usage scenarios. Core i3 is the entry-level option, offering basic performance. Core i5 provides a balanced blend of performance and efficiency, suitable for most tasks. Core i7 is designed for demanding tasks, delivering the best performance and features.
Q: What is Intel Turbo Boost technology?
A: Intel Turbo Boost technology dynamically increases a processor’s clock speed when needed, enhancing performance for demanding tasks. By utilizing the processor’s available thermal headroom, Turbo Boost delivers a temporary performance boost.
Q: How do I check my Intel processor’s model and generation?
A: You can check your processor’s model and generation using the following methods:
- System Information: Open the “System Information” tool (press “Windows key + R” and type “msinfo32”). The processor details are listed under the “System Summary” section.
- Task Manager: Open Task Manager by pressing “Ctrl + Shift + Esc.” Click on the “Performance” tab, and select “CPU.”
- Software Tools: Third-party software like CPU-Z or HWMonitor can provide detailed information about your processor.
Intel Processors List By Generation Pdf
Conclusion
Intel processors have come a long way, and understanding their generations is crucial to make informed decisions. The Intel processor list by generation PDF provided in this article will help you compare features, analyze performance, and choose the right processor for your specific needs. It’s a comprehensive guide that is essential for anyone looking to understand the world of Intel processors.
Are you interested in learning more about a specific Intel processor generation or have any further questions? Let’s discuss in the comments below!





