Imagine this: you’re walking down a busy hospital corridor, medical charts tucked under your arm, when a loud crash echoes from a patient room. You rush inside and find an elderly patient lying on the floor, disoriented and in pain. This scenario, while seemingly dramatic, is a stark reminder of the daily challenges nurses face in protecting their patients from harm. It’s a constant balancing act of providing care while ensuring the safety and well-being of those entrusted to them. But what happens when a patient’s risk for injury is high? That’s where a comprehensive risk for injury nursing care plan comes into play, a critical tool for proactively managing and mitigating potential hazards.

Image: www.vrogue.co
This article delves into the world of risk for injury nursing care plans, exploring their components, implementation strategies, and the vital role they play in promoting patient safety. We’ll uncover the latest trends and best practices, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to develop effective plans that empower you to provide exceptional care while minimizing the risk of injuries.
Understanding Risk for Injury Nursing Care Plans
Defining The Concept
A risk for injury nursing care plan is a comprehensive document that outlines interventions and actions nurses take to prevent potential harm to patients. It’s a proactive approach that identifies individual patient-specific factors contributing to injury risk, including age, mobility, cognitive function, medications, and environmental hazards. These plans are tailored to each patient’s unique needs, ensuring individualized care and a high level of safety.
Components of a Risk for Injury Nursing Care Plan
A well-structured nursing care plan for risk for injury comprises several key components:
- Assessment: The initial step involves a thorough assessment of the patient’s risk factors, including a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and evaluation of their environment. Nurses need to identify potential hazards and consider each patient’s individual vulnerabilities.
- Nursing Diagnosis: Based on the assessment, nurses develop a nursing diagnosis that reflects the patient’s risk for injury. Common diagnoses include “Risk for Falls,” “Risk for Injury Related to Altered Sensorium,” and “Risk for Trauma Related to Unsafe Environment.”
- Goals and Outcomes: The care plan outlines specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that aim to minimize the patient’s risk for injury. These could include reducing fall risk, promoting safe mobility, and enhancing environmental safety.
- Interventions: Interventions are the core of the plan, outlining the actions nurses will take to address the patient’s risk factors. Examples include fall prevention strategies, medication management, frequent monitoring, and education for the patient and family members.
- Evaluation: Ongoing evaluation is crucial to assess the effectiveness of the plan and make necessary adjustments. Nurses regularly monitor patients for any changes in their condition or risk factors and adjust interventions accordingly.
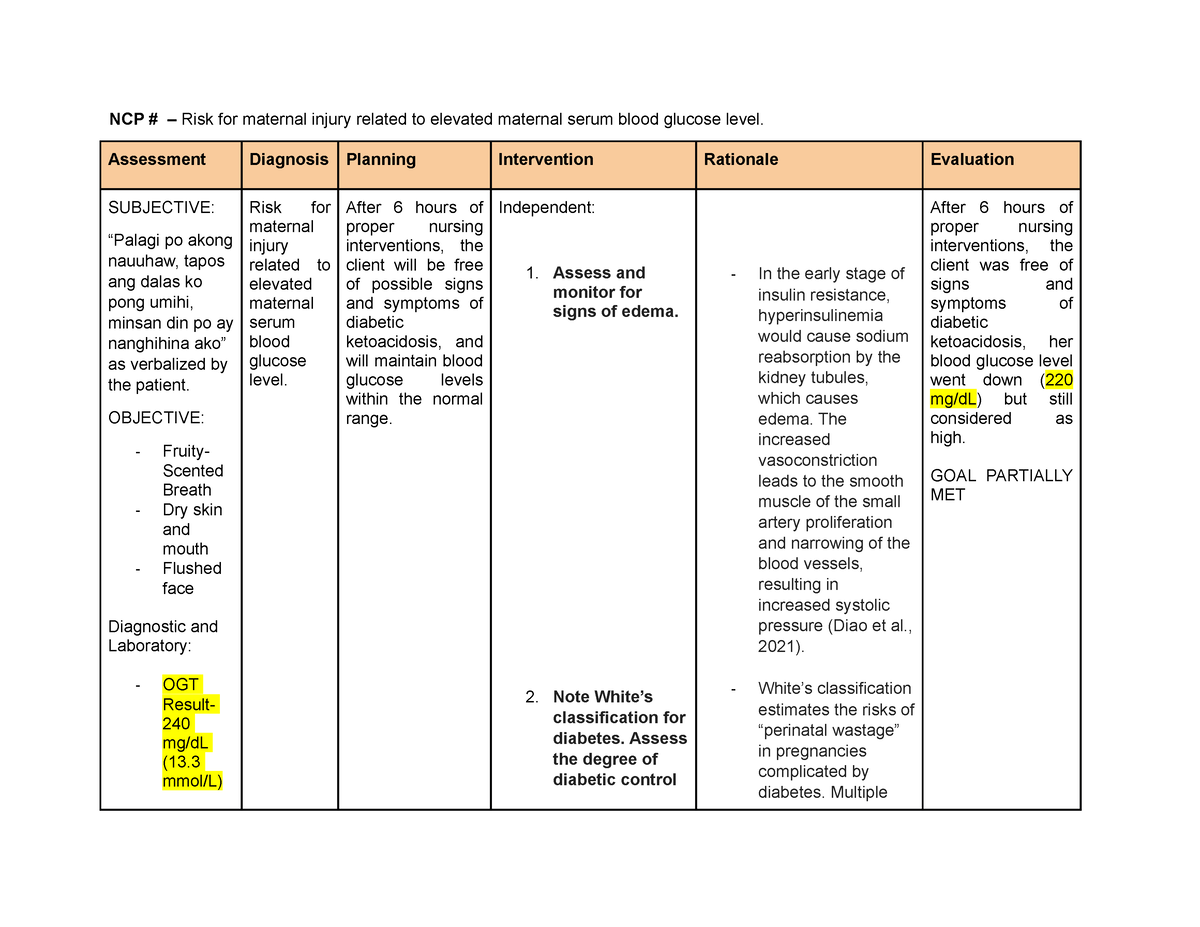
Image: www.vrogue.co
Importance of a Well-Designed Nursing Care Plan
A well-designed risk for injury nursing care plan offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Hospital Readmissions: By proactively addressing risk factors, these plans help minimize the chances of falls, medication errors, and other preventable injuries that could lead to readmissions.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: A comprehensive approach to risk management fosters better patient outcomes, reducing the severity and incidence of injuries.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: The plan’s focus on minimizing hazards and promoting safe practices significantly improves patient safety, fostering a culture of vigilant care.
- Increased Nurse Confidence: A well-structured plan provides nurses with a clear framework for managing risk, increasing their confidence and ability to provide optimal care.
- Improved Communication: Care plans serve as a valuable tool for promoting effective communication among healthcare providers, ensuring consistent implementation of interventions.
Implementing Risk for Injury Nursing Care Plans
Developing Effective Plans
Crafting an effective risk for injury nursing care plan requires a collaborative and multidisciplinary approach. Here’s what it entails:
- Assess the Patient: Conduct a thorough assessment, considering factors like age, history of falls, medications, cognitive status, and environmental hazards. Use standardized tools for fall risk assessment and other relevant screenings.
- Identify Risk Factors: Based on the assessment, identify specific risk factors that might contribute to injury. For example, patients with reduced mobility are at increased risk for falls, while those with cognitive impairment may need additional safety measures.
- Set SMART Goals: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals that address the identified risk factors. Goals may include reducing fall risk, improving patient mobility, or enhancing environmental safety.
- Choose Appropriate Interventions: Select interventions based on the patient’s individual needs and the identified risk factors. This can include fall prevention strategies like gait belts, bed alarms, and medication management. Ensure interventions are tailored to avoid unnecessary restrictions and maintain patient independence.
- Involve the Patient and Family: Encourage patient participation in their care plan. Involve family members in understanding the importance of safety measures and providing support. This collaborative approach fosters shared responsibility and strengthens adherence to the plan.
- Document Thoroughly: Keep meticulous documentation of the assessment, identified risks, interventions, evaluation, and any changes made to the plan. Maintain a clear record of the patient’s progress and any interventions used to address their risk factors.
Best Practices for Implementation
Putting a risk for injury nursing care plan into practice effectively requires adherence to best practices. Here are some key strategies:
- Use Standardized Tools: Leverage standardized tools like fall risk assessment scales and safety checklists to ensure consistent evaluation of risk factors. These tools provide objective measures to guide interventions and track improvement.
- Integrate Technology: Utilize technology like electronic health records to facilitate information sharing, automate reminders for interventions, and track patient progress. This promotes efficiency and improves the safety of care delivery.
- Provide Education and Training: Educate patients, family members, and staff about the importance of risk for injury prevention. Offer clear instructions on safety protocols, medication administration, and any specific precautions relevant to the patient’s condition.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your risk management protocols to identify areas for improvement. Analyze incident reports, assess effectiveness of interventions, and seek feedback from staff. Continuous quality improvement is vital for maintaining patient safety.
Latest Trends in Risk for Injury Nursing Care
The field of risk for injury nursing care plan development is constantly evolving, reflecting advancements in knowledge and technology. Some key trends include:
- Patient-Centered Approach: The emphasis is on empowering patients to participate actively in their care. Nurses encourage patient input, incorporate their preferences, and promote independence within safe boundaries.
- Technology Integration: Smart technology, including wearable devices and sensors, are increasingly utilized to track patient movement, monitor vital signs, and provide real-time alerts for potential falls. This enables proactive intervention and earlier identification of risk factors.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Data analytics is employed to analyze trends in injuries and identify interventions that are most effective in reducing risks. By leveraging data, healthcare providers can make informed decisions to enhance patient safety.
- Focus on Prevention: The focus is shifting from reactive care to proactive prevention. Nursing care plans are increasingly designed to mitigate risk factors before they manifest into actual injuries, promoting a culture of anticipatory safety measures.
Tips and Expert Advice
Based on my experience as a nurse educator and advocate for patient safety, here are some key tips for developing and implementing effective risk for injury nursing care plans:
- Think Holistically: Don’t just focus on falls; consider all potential injuries, including skin tears, medication errors, pressure ulcers, and aspiration. A comprehensive approach ensures a safer environment for all patients.
- Use a Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaborate with physical therapists, occupational therapists, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals to develop tailored interventions that meet the patient’s individual needs.
- Empower the Patient: Encourage patients to actively participate in their care. Explain the importance of safety measures, discuss their concerns, and ensure they understand their role in their own safety.
- Stay Up-to-Date: Continuously seek out new knowledge and evidence-based practices in risk for injury prevention. Attend conferences, read professional journals, and engage with fellow nurses to stay informed about the latest advancements in patient safety.
Remember, a well-executed risk for injury nursing care plan can significantly improve patient safety and foster a culture of proactive care. By embracing a multidisciplinary approach, embracing technology, and continuously evaluating our practices, we can empower ourselves to provide the highest level of care while mitigating potential hazards.
FAQ
Q: Who is responsible for developing a risk for injury nursing care plan?
A: Nurses are primarily responsible for developing and implementing risk for injury nursing care plans, collaborating with other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive and individualized care.
Q: How often should risk for injury care plans be reviewed and updated?
A: Care plans should be reviewed and updated at least once a shift or based on the patient’s changing condition. Regularly assessing the patient’s risk factors, progress, and the effectiveness of interventions is crucial.
Q: What are some common risk factors for injury in hospitalized patients?
A: Common risk factors include age, history of falls, cognitive impairment, mobility limitations, medications that cause drowsiness or dizziness, visual or hearing impairments, and environmental hazards like loose rugs, cluttered walkways, and poor lighting.
Risk For Injury Nursing Care Plan
Conclusion
Developing and implementing effective risk for injury nursing care plans is a cornerstone of patient safety. By consistently assessing patient needs, collaborating with other healthcare professionals, and embracing evidence-based practices, we can provide the highest level of care and minimize the risk of preventable injuries. Remember, every patient deserves a safe and dignified healthcare experience. Are you committed to fostering a culture of patient safety by utilizing risk for injury nursing care plans in your practice?





