Imagine a space, your space. A haven for your hobbies, a workshop for your projects, or even a peaceful retreat away from the everyday hustle. A shed, a humble structure, can be the foundation for just such a sanctuary. But before you dive into the exciting world of shed design and materials, it’s crucial to understand the cost. This is where the concept of “activity 2.2” comes into play, a crucial step in your journey to building a shed that meets your needs and fits your budget.

Image: www.chegg.com
Activity 2.2, often referred to as the “shed cost estimate,” is more than just a number. It’s a roadmap, a blueprint, and a reality check. Without a clear understanding of the financial commitment involved, the dream of your perfect shed might remain just that: a dream. This article delves into the intricacies of activity 2.2, guiding you through the process of formulating a realistic and accurate cost estimate for your shed project.
Defining Your Vision: The Foundation of Activity 2.2
Building a shed isn’t just about throwing up some walls and a roof. It’s about creating a space that serves a specific purpose. This is where activity 2.2 begins. Before you start sketching out those beautiful plans or browsing through lumber prices, take time to define what you truly want from your shed. Think about:
- Purpose: Is it a workspace, a storage solution, a recreational space, or a combination of these? The purpose will drive the size, features, and even the materials you choose.
- Size: How much space do you need? A small 8×10 shed might be perfect for basic storage, while a larger 12×16 structure could accommodate a workshop or a hobby room.
- Features: Do you need windows for light, a door for easy access, electricity, insulation, a loft for extra storage? The more features you include, the higher the cost will climb.
- Materials: Sheds can be built with a variety of materials, each with its own price tag. Wood is a traditional and relatively affordable choice. Metal sheds can be more durable but may be more expensive. Consider the aesthetic and performance demands of your shed.
The Building Blocks of Activity 2.2: Breaking Down Costs
Once you have a clear vision for your shed, it’s time to dive into the nitty-gritty of cost estimation. Activity 2.2 is all about understanding the components that contribute to the overall price, and how these components impact the final cost.
1. The Foundation: A Sturdy Base for Your Shed
Just like any house, a strong foundation is essential for your shed. The type of foundation you choose depends on factors such as soil conditions, local building codes, and the weight of the shed.
Common foundation options include:
- Concrete Slab: This provides a robust and stable base, ideal for heavier sheds or areas prone to moisture. The cost of pouring concrete varies depending on size and local labor rates.
- Concrete Piers: Concrete piers are a less expensive option, suitable for lighter sheds or areas with well-drained soil. They involve strategically placed concrete pillars supporting the shed’s structure.
- Pressure-Treated Wood: Wood foundations are a cost-effective option, but they might require more maintenance over time. Using pressure-treated lumber helps prevent rot and decay in contact with soil.
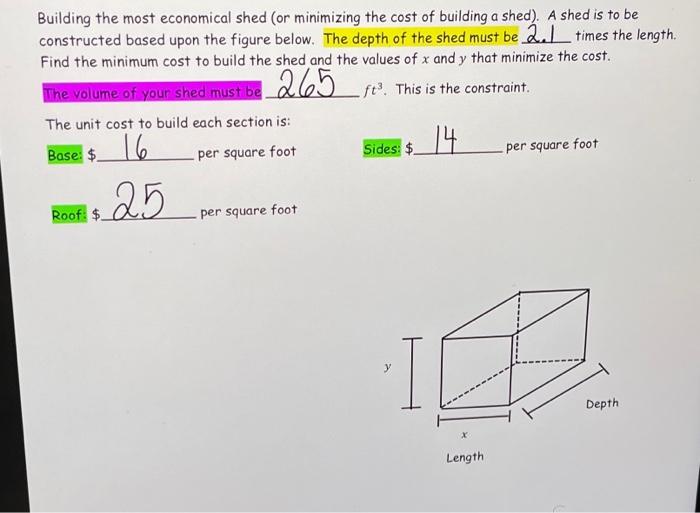
Image: www.chegg.com
2. The Framing: The Skeleton of Your Shed
The framing, the structure that supports your walls and roof, is a significant factor in the overall cost. Wood framing is a common and affordable choice. However, metal framing is becoming increasingly popular, offering durability and resistance to pests and fire.
Cost factors to consider:
- Framing Material: Wood framing is readily available and typically less costly than metal framing.
- Size and Complexity: A larger shed, or one with intricate designs, will require more framing materials.
- Quality: Using higher-quality lumber or metal framing can increase the cost but offer greater longevity and resistance to warping and decay.
3. The Roof: Protection from the Elements
The roof plays a vital role in protecting your shed from rain, snow, and sun. It’s a crucial element to consider in your cost estimation.
Cost factors to consider:
- Roof Covering: Common roof covering materials include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and even green roof systems. Each has its own pros and cons in terms of cost, durability, and aesthetics.
- Roof Pitch: A steeper roof pitch is more expensive to build but offers better drainage and can accommodate heavier snow loads.
- Roof Framing: The size and complexity of the roof framing can also influence the overall cost.
4. The Siding and Windows: Aesthetics and Functionality
Siding, the protective outer layer of your shed, contributes to both its appearance and weather resistance.
Cost factors to consider:
- Siding Material: Options range from affordable vinyl siding to more luxurious wood siding or metal panels. The choice will greatly influence the final cost.
- Windows: Adding windows can enhance natural light and ventilation but will increase the expense. The number, size, and type of windows will play a role in cost calculation.
5. The Doors: Access and Security
The door is crucial for accessing your shed and maintaining its security.
Cost factors to consider:
- Door Type: Single, double, sliding, or overhead garage doors all have different costs. Consider the ease of access and security needs.
- Door Material: Wooden doors are affordable but may require more maintenance. Metal doors are more durable but might be more expensive.
6. Other Considerations: Adding Details to Your Activity 2.2 Estimate
Beyond the basic building elements, several other factors can influence the cost of your shed.
- Insulation: Adding insulation to your shed enhances comfort and energy efficiency but adds to the cost. Consider the climate you live in when making this decision.
- Electricity: Running electricity to your shed will involve installing wiring, outlets, and potentially a sub-panel. This can significantly increase the overall cost.
- Flooring: While a concrete slab typically serves as the floor, adding a finished floor such as wood or tile will increase the cost.
- Finishing Touches: Consider the costs of painting the exterior, adding trim, and incorporating personal touches like flower boxes or decorative lighting.
Beyond Activity 2.2: Factors That Can Affect Your Shed’s Cost
Once you’ve built a preliminary cost estimate using Activity 2.2, it’s important to acknowledge external factors that can impact the final price.
- Location: Building costs can vary significantly depending on where you live. Labor rates, material availability, and local regulations all play a role.
- Seasonality: Building materials might be more expensive during peak construction seasons. Planning ahead can save you money in the long run.
- Labor: The cost of labor depends on the complexity of your shed and the availability of qualified contractors in your area.
- Permits: Some localities require building permits for shed construction, which can add an additional expense to your budget.
- Unexpected Expenses: Always factor in a contingency for unexpected expenses. These can arise from unforeseen issues during construction or a sudden increase in material prices.
Activity 2.2 2 Shed Cost Estimate
Activity 2.2: A Tool for Success
Activity 2.2, the shed cost estimate, is more than just a number-crunching exercise. It’s a key step in bringing your dream shed to life. By carefully considering all the elements that go into building your shed, from the foundation to the finishing touches, you’ll be able to create a budget that aligns with your needs and financial capabilities. Remember, it’s better to be prepared with a realistic cost estimate than to face unexpected expenses during the construction process.
Armed with this knowledge, you can now embark on your shed-building journey with confidence. So, embrace Activity 2.2, use it as a guide, and enjoy the process of creating a space that perfectly reflects your own unique vision.





